.

The Rise of CO₂ Extraction in the Cannabis Industry
CO₂ extraction has taken over the cannabis and CBD industry. This newer technology is friendlier to the environment, non-toxic, and non-flammable. Supercritical CO₂ works as both a liquid and a gas to efficiently extract as many terpenes and cannabinoids as possible. Find out how it works below.
Contents:
- What is supercritical co₂ extraction?
- How are co₂ extractions performed?
- Supercritical vs subcritical co₂ extraction
- Co₂ extraction: step-by-step process
- Where is supercritical co₂ extraction used, besides cannabis?
- What are the benefits of using co₂?
- What products can be made in the cannabis industry using co₂ extraction?
- Bho vs co₂ extraction
- ? How much does a CO₂ extractor cost?
- CO₂ extractors are pricey, costing between $135,000 and $150,000 per unit.
- ??? How much do CO₂ extractors yield?
- CO₂ extraction offers a return of between 4–7%. If you start out with 100g of trimmed material, you can expect a yield of 4–7g of oil following the extraction.
- ??♂️ Which is better, CO₂ extraction or cold-pressed oils?
- CO₂ extraction produces a superior product to cold-pressed techniques. CO₂ extractors prevent contact between plant material and oxygen, helping to keep terpenes and cannabinoids intact.
- ? Is CO₂ extraction healthy?
- CO₂ extraction eliminates the risk of harmful solvent residues and creates a much purer product than butane, propane, and other solvents.
CO₂ extraction has taken the cannabis industry by storm. Unlike older extraction methods, CO₂ extraction eliminates the risk of residual solvent winding up in the end product. This newer method also produces higher-quality extracts overall.
By manipulating temperature and pressure levels, CO₂ extraction is used to pull terpenes, cannabinoids, and other components out of plant matter with minimal disturbance and oxidation. The result? A phytochemical mix that maintains the true taste, smell, and essence of the original strain used.
Using this technology, manufacturers are crafting CBD oil, terpene blends, and full-spectrum extracts that are purer and more potent than ever before. Discover why extract producers are choosing supercritical CO₂ above all else, what exactly takes place during the process, and how to make CBD oil using CO₂.
What Is Supercritical CO₂ Extraction?
The words “supercritical CO₂ extraction” probably conjure mental images of mad scientists carrying out complex scientific procedures in underground bunkers. Although the term sounds complex and even intimidating, you’ll find it easy to understand when we break it down.
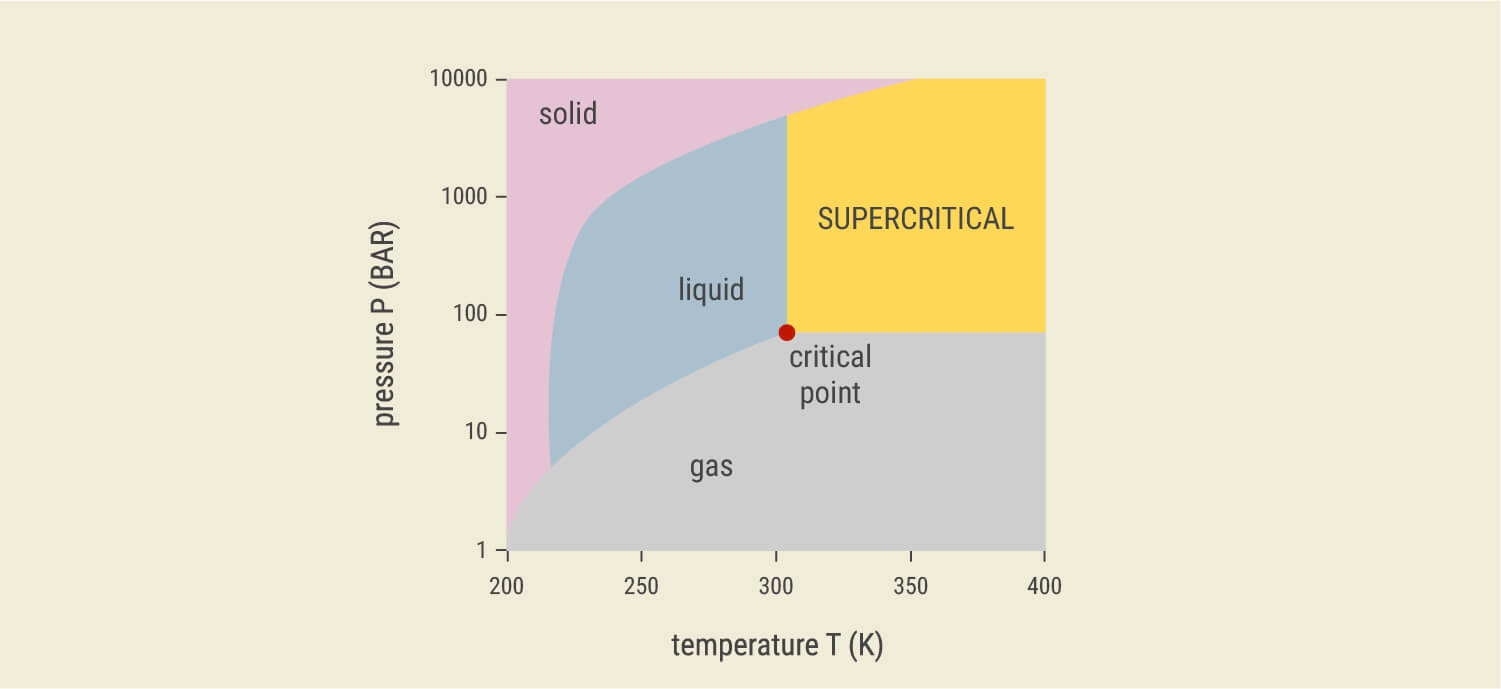
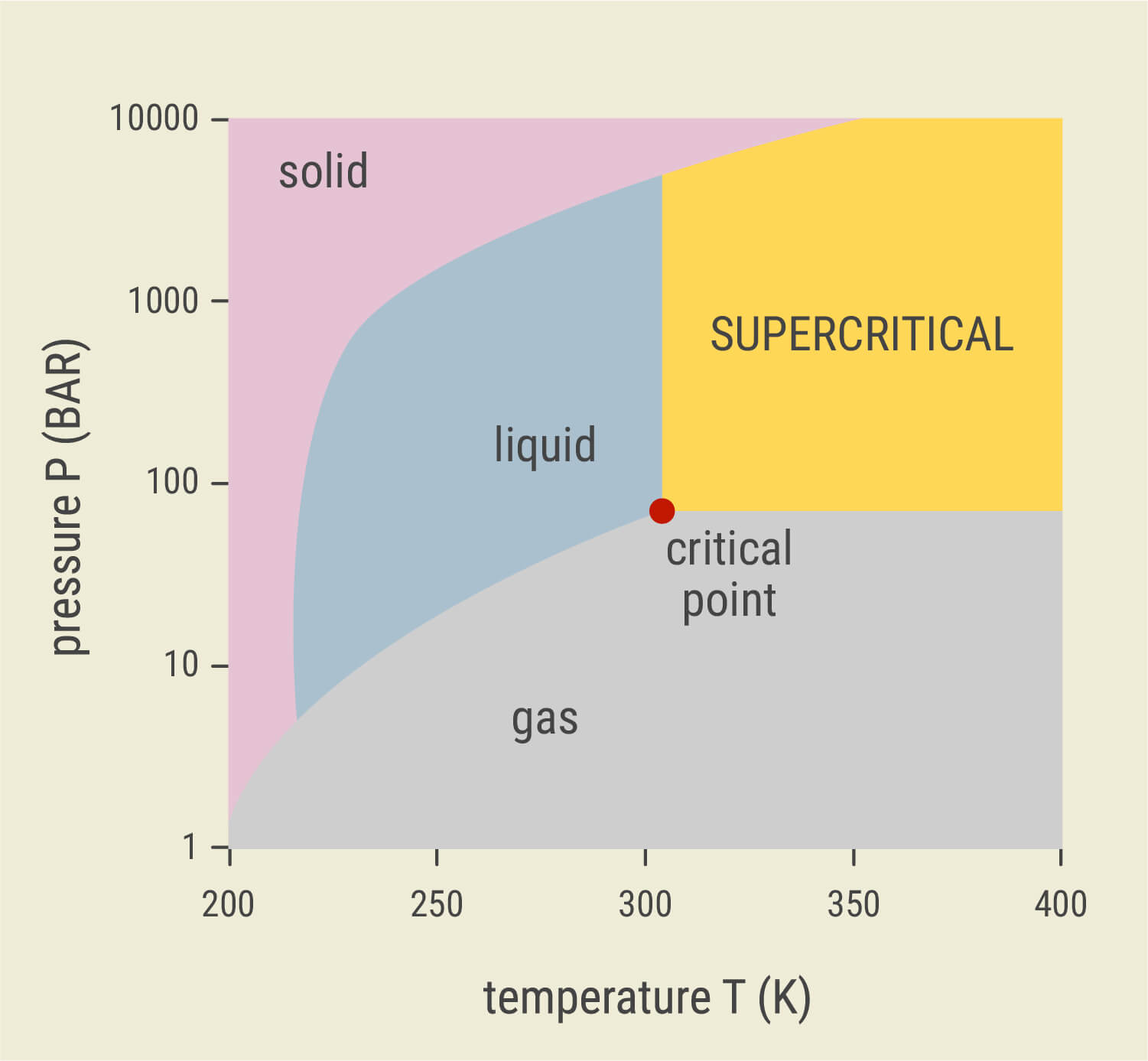
CO₂ (carbon dioxide) exists as a solid, liquid, or gas depending on the external environment. For CO₂ to exist as a solid, it must experience 1 atmosphere of pressure (the same amount of pressure we walk around in) and extremely cold temperatures of -78.5°C.
These environmental factors create dry ice, a solid form of carbon that turns into a gas at music concerts and nightclubs, making everything look mysterious and awesome. Carbon turns into a gas precisely when temperatures exceed -78.5°C.
Carbon can also exist as a liquid, but much more extreme environmental conditions are required to achieve this state. Liquid carbon only occurs under 100 atmospheres of pressure, and at temperatures of around -40°C.
So, where does supercritical carbon dioxide come into the equation? The term “supercritical” simply refers to carbon in a form where it exhibits the properties of both a liquid and a gas simultaneously.
CO₂ extractors use a combination of pressure and temperature to force carbon past its “critical point”. This happens at a pressure of 100 atmospheres and temperatures of around 27°C.
Once forced into its supercritical state, CO₂ becomes a green organic solvent. It boasts non-flammable, non-toxic, and inert properties, yet effectively extracts compounds such as cannabinoids, terpenes, and other cannabis constituents.
-
How To Make CBD Oil Using Supercritical CO₂ Extraction
As a gas, supercritical CO₂ can pass between very small gaps in plant matter, and as a liquid it can pull phytochemicals in as it goes. When it comes to making CBD oil, technicians simply load up these machines with high-CBD hemp flowers that possess almost no THC.
As the supercritical CO₂ passes through the buds, it picks up high quantities of CBD and terpenes, which are then infused into a carrier oil at the end of the process.
How Are CO₂ Extractions Performed?
CO₂ extraction is carried out using large and extremely expensive industrial units consisting of a series of chambers and tubes. Because of their size and cost, only companies willing to make a large investment can use this technology to create top-tier cannabis extracts.
For now, most amateur extract creators are limited to high-proof alcohol extractions. However, the first computer was over 15 metres long, and now you carry more sophisticated technology around in your pocket.
In other words, years down the line, you might find yourself loading a home CO₂ extractor with your latest harvest to make some of the cleanest CBD oil you’ll ever consume. But in the present reality, CO₂ extractors remain bulky and consist of many parts, including CO₂ tanks, pumps, extractor vessels, separators, and a collection vessel.
Supercritical vs Subcritical CO₂ Extraction
Before we delve into the step-by-step process of supercritical extraction, let’s explore the difference between supercritical and subcritical extraction.
As you’ve learned, carbon enters a supercritical state when it passes its critical point. In contrast, subcritical conditions occur below the critical point, at lower temperatures (“sub” means “below”).
Because the carbon doesn’t rise above this critical point, but still experiences enormous amounts of pressure, it remains a liquid. As a pure liquid, carbon still works as an effective solvent. However, because it doesn’t display the behaviour of gas, it doesn’t move through plant material in quite the same way.
Therefore, subcritical carbon dioxide is less effective as a solvent, meaning it doesn’t take up as many constituents as supercritical CO₂. But this form of extraction also comes with some benefits.
Because it uses lower temperatures, subcritical CO₂ extraction preserves some of the more volatile terpenes found within cannabis; those that begin to degrade at the relatively mild temperature used to conduct supercritical CO₂ extraction. Essentially, subcritical CO₂ extraction can create terpene-rich products that aren't possible through other means.
Overall, supercritical CO₂ extraction has won the favour of the cannabis industry for its efficiency. Although some terpenes may degrade, many stay intact, and this form of extraction simply pulls out more constituents with every run.
CO₂ Extraction: Step-by-Step Process
Supercritical CO₂ extractors require trained technicians to operate. The process takes place over four main phases.
-
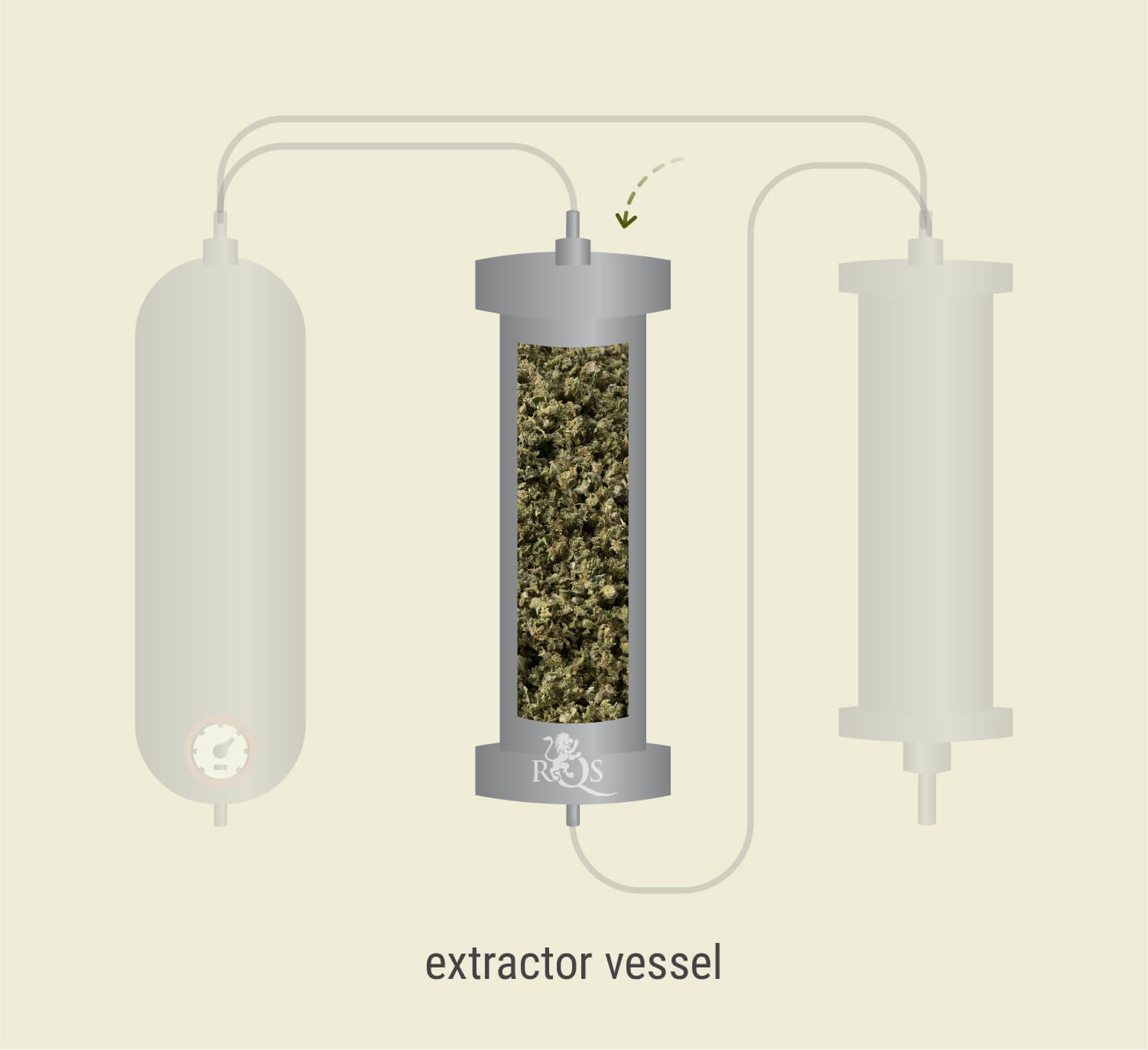
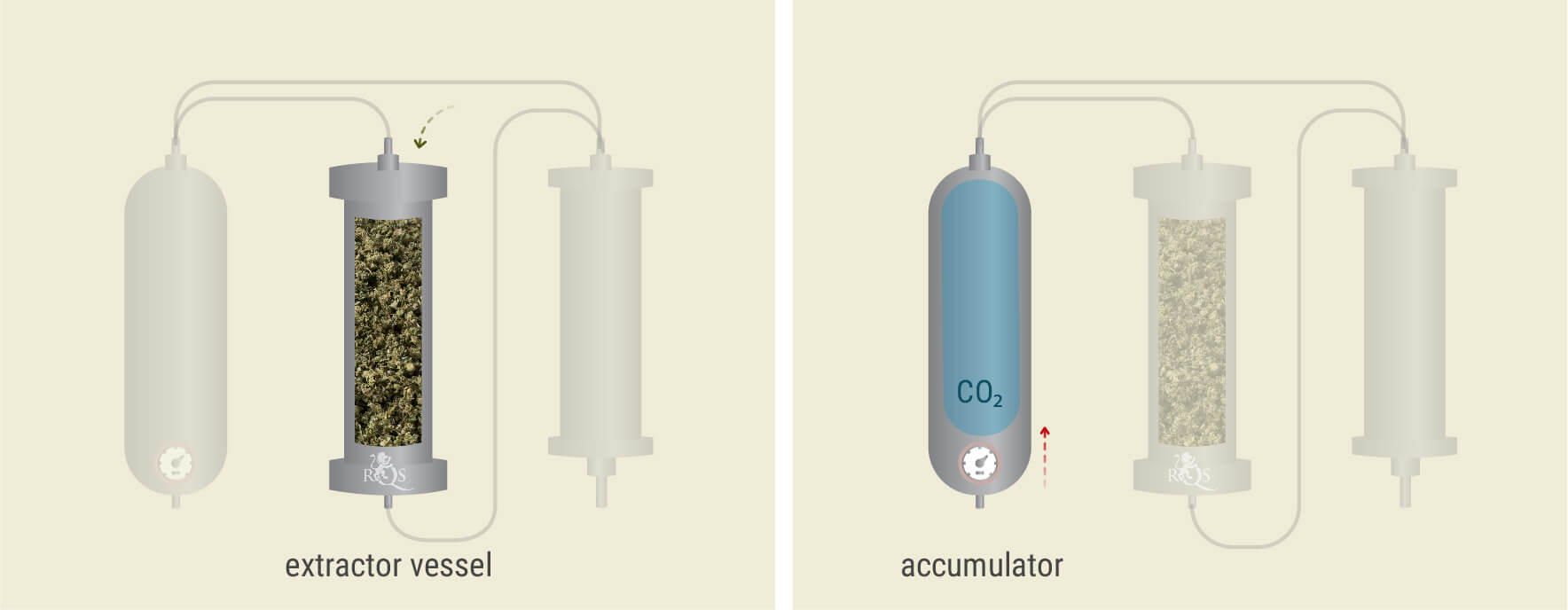
Plant Matter Enters the Vessel
During the first stage, technicians load up the extraction vessel—a large metal tube—with plant matter. To fill the column to maximum capacity, the flowers are often first processed into finer particles.
As well as increasing capacity, this action increases the surface area, which allows the solvent to gather more of the desired molecules.

-
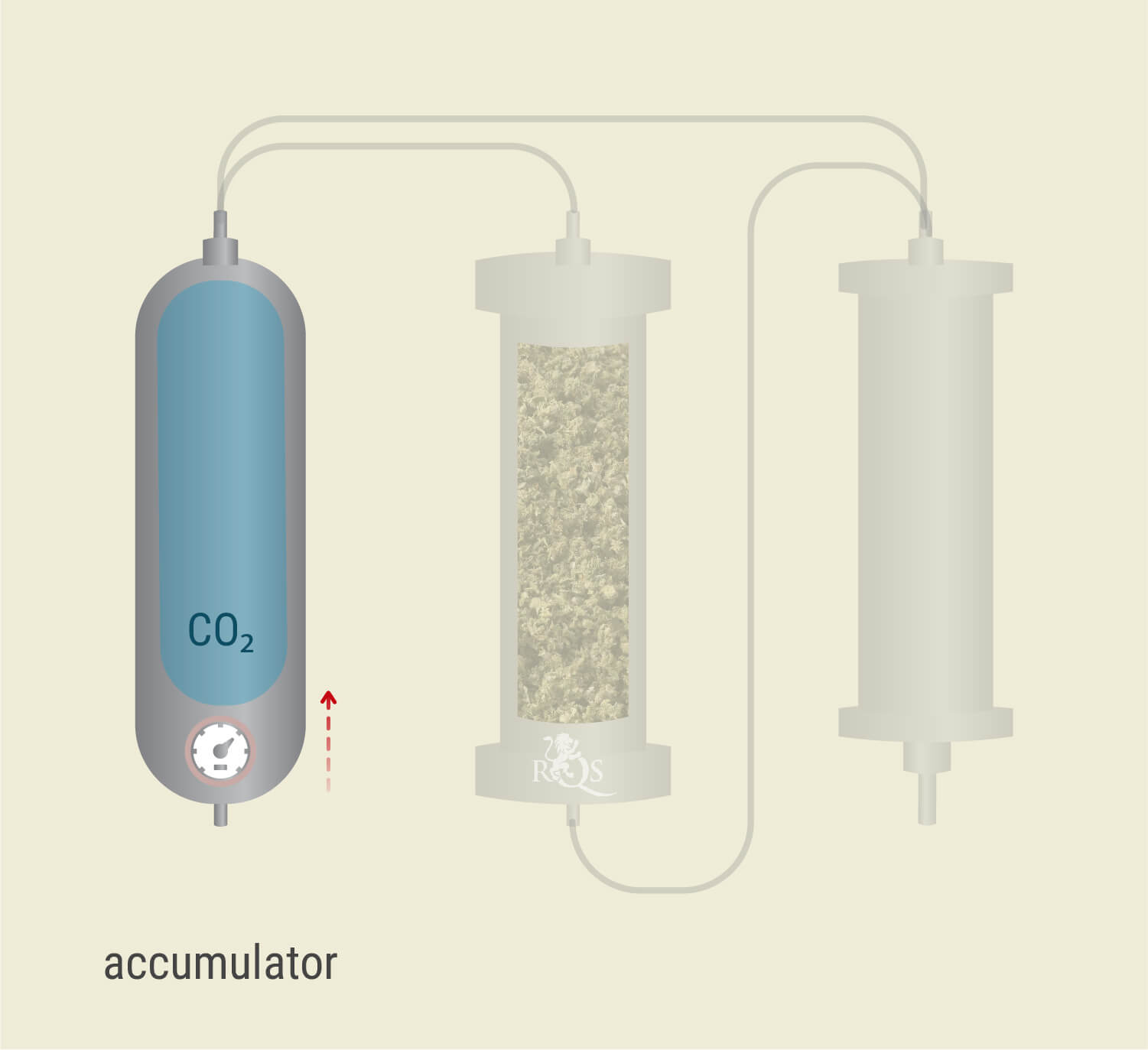
CO₂ Exceeds Its Critical Point
After filling up the extraction vessel, the technicians proceed to change the settings on the extractor, releasing liquid CO₂ into a part of the machine called the accumulator.
By increasing the temperature and pressure within this part of the extractor, they expose the liquid CO₂ to the conditions at which it passes the critical point and enters a supercritical state.
-
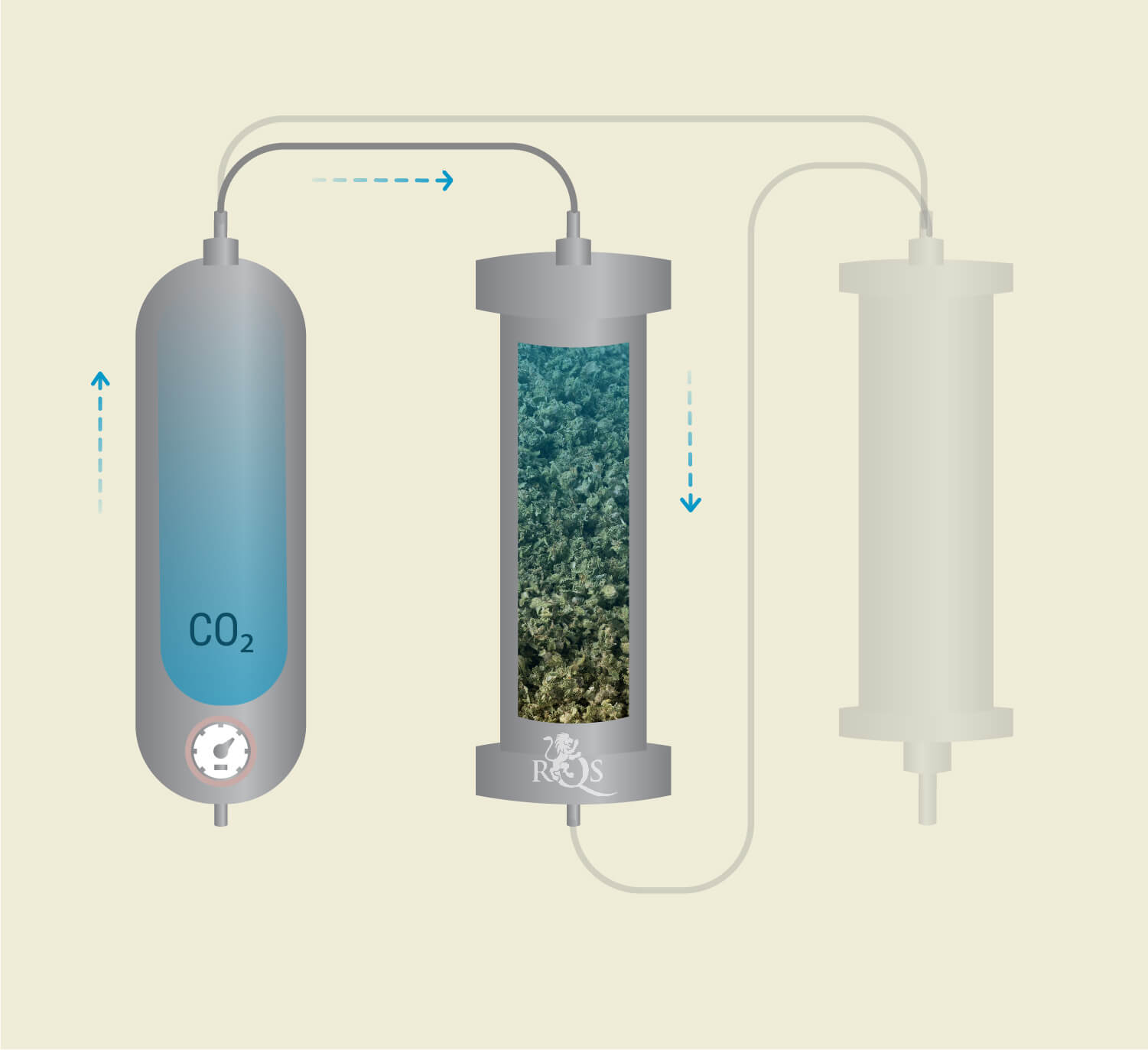
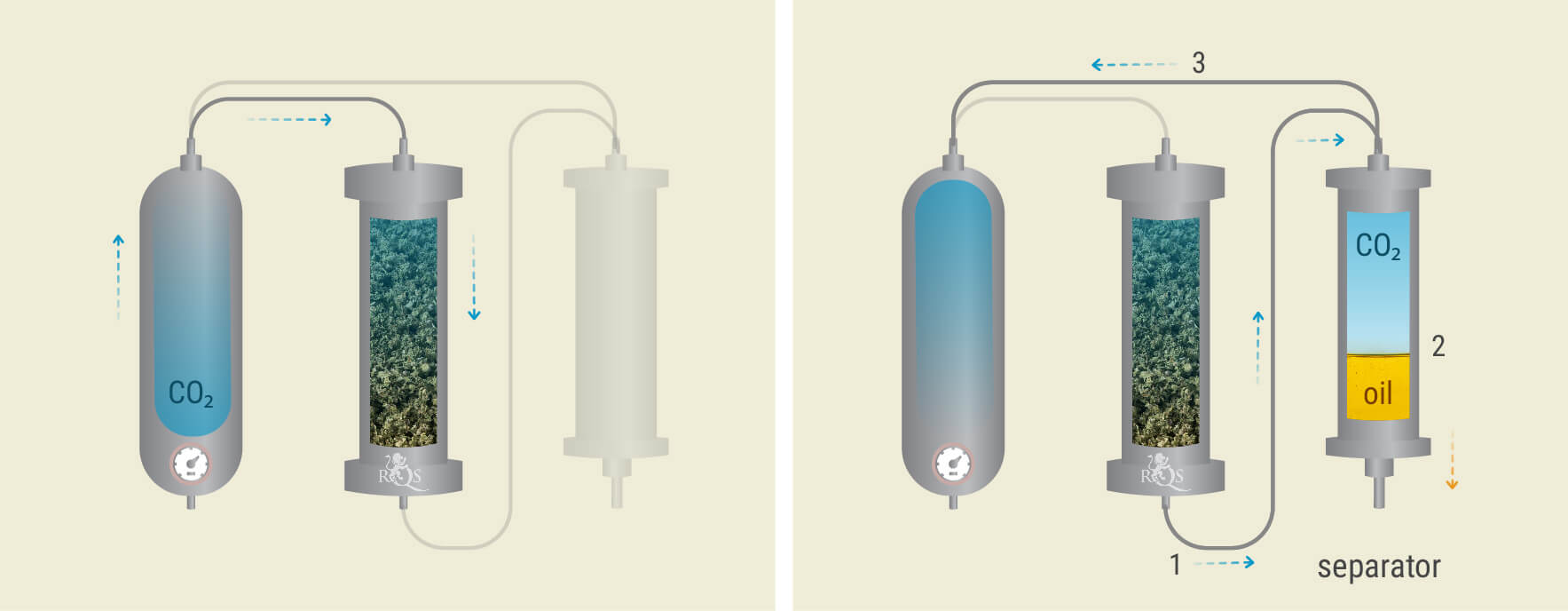
Supercritical CO₂ Becomes Infused With Phytochemicals
The supercritical CO₂ then leaves the accumulator and enters the extraction vessel—the column loaded with processed plant matter.
With the properties of a gas, the substance squeezes through the tiniest gaps between the plant matter. With the properties of a liquid solvent, it absorbs prized molecules such as THC and CBD, and terpenes such as pinene and myrcene.

-
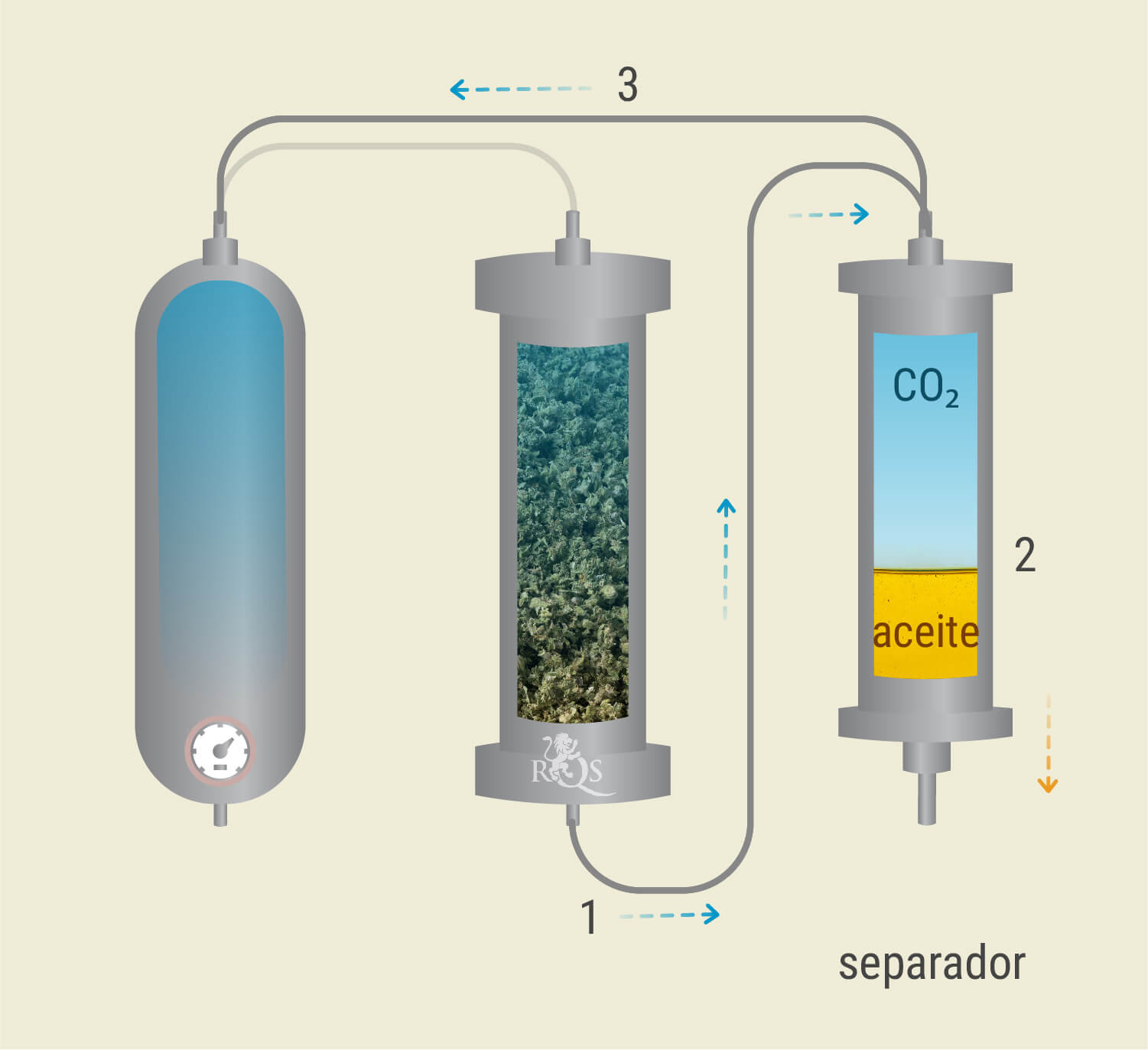
Phase Exchange
After passing through the extraction vessel, picking up cannabinoids and terpenes as it goes, the supercritical CO₂ passes through a tube at the bottom of the vessel into the separator. A change in temperature and pressure causes the cannabis molecules to separate from the CO₂ and form an oil.
The less-dense CO₂ passes through the top of the separator where it becomes a liquid once more, ready for another run in the future. The magic of closed-loop systems is that the CO₂ is recaptured and nothing goes to waste.
Finally, technicians take the oil and use it to create an array of cannabis products. For example, when making CBD oil, they’ll dilute the product with a carrier oil such as olive oil or hemp seed oil.
The properties of the product depend largely on the initial material used. Flowers high in THC will produce psychotropic THC extracts, whereas those high in CBD will produce non-psychotropic CBD extracts.
Where Is Supercritical CO₂ Extraction Used, Besides Cannabis?
Although quite new to the world of cannabis, other industries have used this efficient, green, and safe form of extraction for decades. Supercritical CO₂ extraction first appeared in the 1980s, and has since enhanced the extraction process of many different sectors within the food and beverage industry.
Coffee companies adopted the technology very early on to remove caffeine from their products and create decaffeinated coffee. Other companies use CO₂ extractors to remove trichloroanisole from corks. This compound adds an unpleasant taste to wine, and the removal of it has led to the production of billions of aroma-free corks.
Scientists have also tested the ability of CO₂ extraction to obtain antioxidants such as anthocyanins from blueberries and other fruits. These compounds are used in drinks, supplements, and even as pigments to colour edible products.
Many retailers are now including “CO₂ extracted” on their product labels to display their commitment to purity and greener manufacturing processes.
What Are the Benefits of Using CO₂?
Supercritical CO₂ extraction offers a whole host of benefits. These advantages are precisely why many cannabis companies are investing in this technology over older methods. Check out the main benefits below.
| Natural | Above all else, both manufacturers and consumers see CO₂ as more of a natural choice. This element occurs throughout nature, and our bodies produce it every second of the day. |
| FDA Approved | Confidence in supercritical CO₂ extraction surged following its approval as a safe solvent[1] by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). |
| Non-Toxic | Supercritical CO₂ extraction won this status partly because of its non-toxic nature. Unlike solvents such as butane, CO₂ is safe for both human health and the environment. |
| Clean and Pure | Supercritical CO₂ extractors are designed to recover all of the liquid CO₂ present in the machine before the extraction takes place. This means the extracts that emerge from the other end are free of solvent residue and perfectly pure. |
| Non-Flammable | You’ve likely heard stories of people blowing the roofs off their homes when performing butane cannabis extractions. These accidents occur because of the flammable nature of the gas. CO₂ sidesteps this dangerous process altogether. |
| Natural |
| Above all else, both manufacturers and consumers see CO₂ as more of a natural choice. This element occurs throughout nature, and our bodies produce it every second of the day. |
| FDA Approved |
| Confidence in supercritical CO₂ extraction surged following its approval as a safe solvent[1] by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). |
| Non-Toxic |
| Supercritical CO₂ extraction won this status partly because of its non-toxic nature. Unlike solvents such as butane, CO₂ is safe for both human health and the environment. |
| Clean and Pure |
| Supercritical CO₂ extractors are designed to recover all of the liquid CO₂ present in the machine before the extraction takes place. This means the extracts that emerge from the other end are free of solvent residue and perfectly pure. |
| Non-Flammable |
| You’ve likely heard stories of people blowing the roofs off their homes when performing butane cannabis extractions. These accidents occur because of the flammable nature of the gas. CO₂ sidesteps this dangerous process altogether. |
What Products Can Be Made in the Cannabis Industry Using CO₂ Extraction?
Manufacturers can create a whole host of cannabis products using this extraction technology. Dispensary shelves are already filling up with a diverse range of CO₂-extracted products, including:
- CBD oil
- THC isolate
- CBD isolate
- Full-spectrum extracts
- Wax
- Dabs
As researchers continue to unveil the full range of cannabinoids and terpenes within the plant, we can expect to see more CO₂-extracted cannabis products appear in the near future.
BHO vs CO₂ Extraction
CO₂ extraction outperforms butane hash oil (BHO) extraction at almost every level. To start, the former uses much lower temperatures during the process, which helps to preserve those precious and tasty terpenes.
Moreover, the use of butane poses a long list of potential problems. If it ends up in the final product, it poses a serious health hazard. Plus, butane as a solvent poses the risks of fire and explosion when handled incorrectly.
Currently, BHO only wins on one point: affordability. However, as CO₂ extraction technology becomes cheaper and more accessible, it will surely make its way into households in the coming years.
- Recent Advances in Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Natural Plant Materials https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov