Cannabis Grow Guide by Royal Queen Seeds
Cannabis Grow Guide by Royal Queen Seeds
- Growing cannabis step by step
- Cannabis growing basics
- Choosing your seeds
- How to germinate seeds
- The cannabis vegetative stage
- The cannabis flowering stage
- Harvesting cannabis
- Trimming, drying, and curing
- Choosing pots and soil
-
Growing indoors
- A Complete Overview Of Growing Cannabis Indoors
- Cannabis Cultivation Tips: How To Set Up Indoor Grow Lights
- How Many Cannabis Plants Can You Grow Per Square Metre?
- Indoor Cannabis Growing: Relative Humidity and Temperatures
- Hydroponics Cannabis Growing Guide (with diagrams)
- Cannabis Micro Growing: Growing Great Weed in Tiny Spaces
- Growing outdoors
- How to grow autoflowering cannabis
- Cannabis nutrients and pH
- Cannabis troubleshooting: Nutrients
-
Cannabis troubleshooting: Growing
- Cannabis Seed Germination — Troubleshooting Guide
- How to Deal With Pythium (Root Rot) in Cannabis Plants
- Slow Cannabis Plant Growth And What You Can Do About It
- How to Deal With Leggy Cannabis Seedlings
- Watering Your Cannabis: How to Fix Overwatering and Underwatering
- Understanding Male, Female, And Hermaphrodite Cannabis
- Identifying and Treating Common Cannabis Ailments
- How To Revive a Sick Cannabis Plant
- How to Avoid Mouldy Weed During Drying and Curing
- How to Prevent and Treat Dry and Crispy Cannabis Leaves
- What Cannabis Leaves Can Tell You
- Causes and Solutions for Yellow Cannabis Leaves
-
Cannabis Strains Grow Report
- HulkBerry Automatic Grow Report
- Blue Cheese Auto Grow Report
- Purple Punch Automatic Strain Grow Report
- Triple G Automatic Grow Report
- Do-Si-Dos Automatic Grow Report
- Green Gelato Automatic Grow Report
- Haze Berry Automatic Grow Report
- Purple Queen Automatic Grow Report
- Cookies Gelato Automatic Grow Report
- Sherbet Queen Automatic Grow Report
- Sweet Skunk Automatic Grow Report
- Medusa F1 Grow Report
- Cannabis plant training
-
Weed growing tips
- The Cannabis Plant Anatomy
- How to preserve seeds
- How Much Sunlight Do Outdoor Cannabis Plants Need To Grow?
- How to Control and Prevent Stretching in Cannabis Plants
- My Cannabis Plants Are Growing Too Tall: What Should I Do?
- Should You Worry About Purple Or Red Cannabis Stems?
- What To Do When Your Indoor Cannabis Won’t Flower
- How To Protect Your Cannabis Plants From Heat Stress
- How To Tell If Your Female Cannabis Plant Has Been Pollinated
- Growing Medical Marijuana
- Bud Washing: How to Clean Your Weed
- Understanding Cannabis Yield per Plant

Slow Cannabis Plant Growth And What You Can Do About It
“Why are my plants growing so slow?”. Sometimes, marijuana plant problems occur out of the blue. Your baby may not have shown any signs of an issue, but now you notice that development has halted and have no idea why. Here are some possible factors behind the slowed growth of your cannabis seedling or plant.
Contents:
- Reasons for slow or stunted cannabis growth
- Seeds are old or low-quality
- Clone stress
- Root health
- Cannabis plants stretch too much
- Plants are not getting enough light
- Plants are getting too much light
- Incorrect light spectrum
- Light stress: dark cycle interruption
- Overwatering
- Not enough nutrients
- Calcium deficiency
- Incorrect pH level
- Temperatures are too low or too high
- Planting pots are too big
- Stress caused by pests / diseases
- Stress caused by tissue damage
- Stress from cannabis training techniques
- Age stress
18 Reasons for Slow or Stunted Cannabis Growth
1. Seeds Are Old or Low-quality
Old seeds don’t just take longer to germinate (if they germinate at all); plants grown from aged seeds can also sometimes grow at a reduced pace. Likewise, good genetics are essential for healthy and vigorous growth from seed to harvest. A random bagseed will not perform nearly as well as quality seeds obtained from a reputable seedbank.
2. Clone Stress
Sometimes cuttings don’t root well, which hampers their growth. To prevent this from happening, apply a little bit of rooting hormone immediately after taking your cuttings.
Also, make sure your environment promotes root growth. The medium should be humid (but not too moist) with a pH level of about 6.0.
Keep your cuttings at a temperature of around 22ºC. If they get too cold, they won’t root at all, and if it’s too hot, the roots will die.
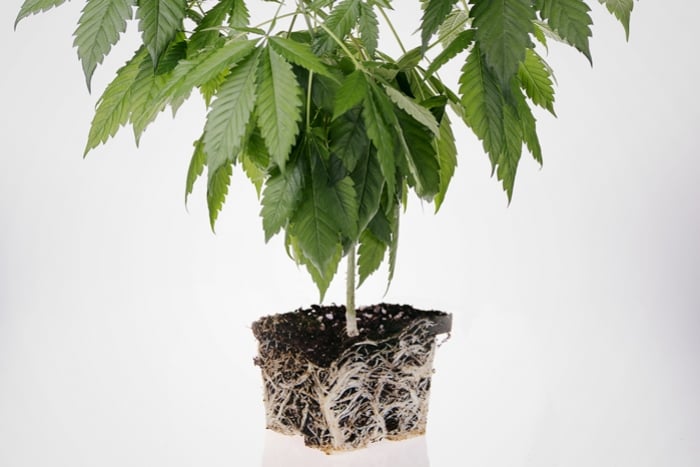
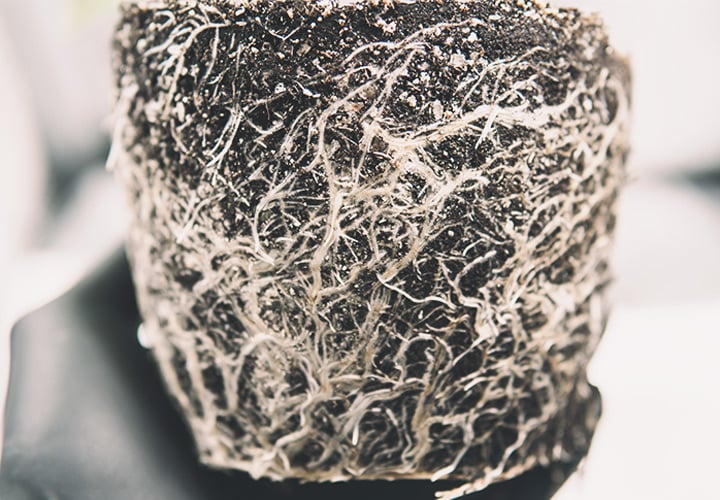
3. Root Health
When your plant’s roots can’t receive enough oxygen, metabolic functions slow down. In some cases, a lack of oxygen may stop their growth altogether. One common reason for this is overwatering or using substrates with poor drainage.
What to do about it? Create a light and airy growing medium with good drainage. You can improve poor-draining soil by adding some perlite.
The root zone for your cannabis plants should never get much hotter or colder than room temperature. Likewise, physical damage to the roots, mould, or bacteria can severely affect the growth of your plants. Always use non-transparent planters so light doesn’t reach the roots, as this is bad as well.


4. Cannabis Plants Stretch Too Much
Stretching among seedlings can be particularly problematic. Multiple factors can induce this response, but the most likely culprit is a lack of light.
If your seedlings are spindly, increase light intensity or bring the lights closer. Prop them up with dowels as an aid during recovery. As a last resort, you can (carefully) replant them deeper into a new pot.
5. Plants Are Not Getting Enough Light
Although requirements can vary from strain to strain, light is nonetheless a critical factor for the development of all cannabis plants. A lack of “good” light can absolutely lead to slowed growth. If you grow indoors and suspect that your plants aren’t getting enough light, try to decrease the distance between your lamps and the tops of plants. If you grow outdoors in pots, move your plants to a sunnier spot.
6. Plants Are Getting Too Much Light
Any type of stress on your cannabis plants, including many hours of exposure to direct sunlight without rest, can also halt or slow down growth. If you grow indoors and suspect light exposure to be the source of stress, decrease the intensity or move lamps further away from the canopy if possible. Know that seedlings are particularly sensitive to intense light! If you grow outdoors and you’re able to, move your plants into a spot where the light is diffused, such as around a shade tree.
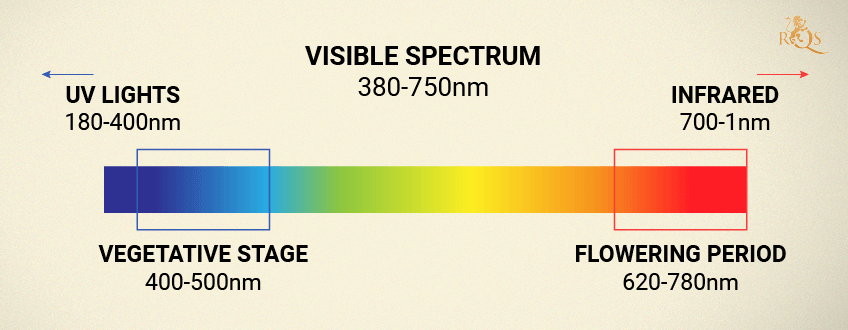
7. Incorrect Light Spectrum
How fast and how vigorously plants grow are influenced by the spectrum of light they receive. Make sure you use the correct type of light according to each stage of growth. For healthy vegetative growth, you want a cooler light with more blue in its spectrum, a so-called "vegging light". Lights with a warmer, more reddish spectrum are used for the flowering phase.
8. Light Stress: Dark Cycle Interruption
Light is essential for all plants to grow. Any changes in light intensity or exposure will have an effect on growth. Flowering cannabis is especially susceptible to interruptions in the dark cycle. A light leak in your tent, stray light from a street lamp, and even a red light from a camera can disrupt flowering, and in a worst case scenario, can turn plants hermaphroditic. For that reason, it is very important to maintain complete darkness during the lights-off hours.
Exposing weed plants to irregular light hours can cause a hormone imbalance that confuses their internal clock.
Your plants could flower prematurely, or they could revert back to the vegetative stage. If this happens, growth and yields will greatly suffer. For that reason, make sure to keep your light cycle consistent.
The above suggestions predominantly apply to photoperiod strains, as autoflowering cannabis flowers based on age rather than light exposure.
9. Overwatering
Overwatering is one of the most common mistakes made by new cannabis growers. It’s like suffocating your plants, and one of the main reasons behind slow growth, nutrient deficiencies, root rot, fungus, and many other problems. Don’t water too often and do not water on a fixed schedule. It is better water less frequently so that the soil can dry out between waterings. A good way to test whether you should water or not is to lift up the pot itself. If it feels quite light, it is time to water again.
10. Not Enough Nutrients
Although not as common as overfeeding cannabis plants, an insufficient amount of nutrients for healthy growth can well be the reason for slow growth. Know that the nutrients found in most commercial potting mixes will only last for 3–4 weeks; afterwards, you will have to administer some more quality nutrients. Check the label of your nutrient products for the recommended dosage for healthy growth. Also know that your plant’s nutrient requirements are closely linked to the light intensity your plants are exposed to. Plants under intensive lights grow faster and will require more nutrients than plants under fluorescent lights, for example.
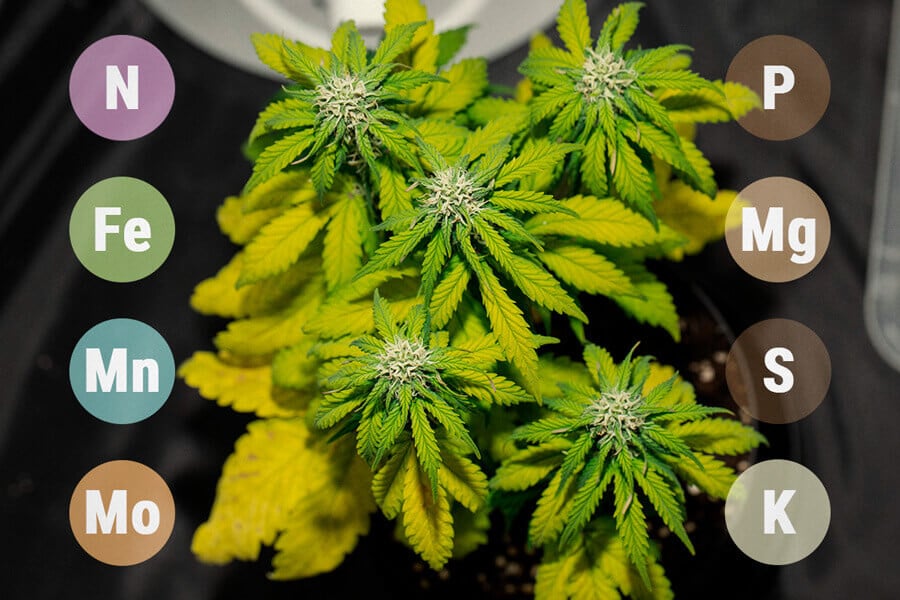
11. Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is among those vital elements that your plant needs for healthy development. A lack of calcium can manifest in the following symptoms:
- Fresh growth is slow, twisted, and curled
- Young shoots are discoloured and turn purple or yellow
- Overall plant growth is slow and lacks vigour and vitality
- You can avoid a calcium deficiency by adding dolomitic lime to your soil or growing medium
Address a calcium deficiency immediately with commercial CalMag products that contain liquid calcium. You can add these products to your nutrient solution or administer them as a foliar spray.
Be aware that some growing media, like coco, increase the risk for a calcium deficiency. If you grow in coco, you should use special coco nutrients and/or regularly add CalMag to your nutrient regimen.
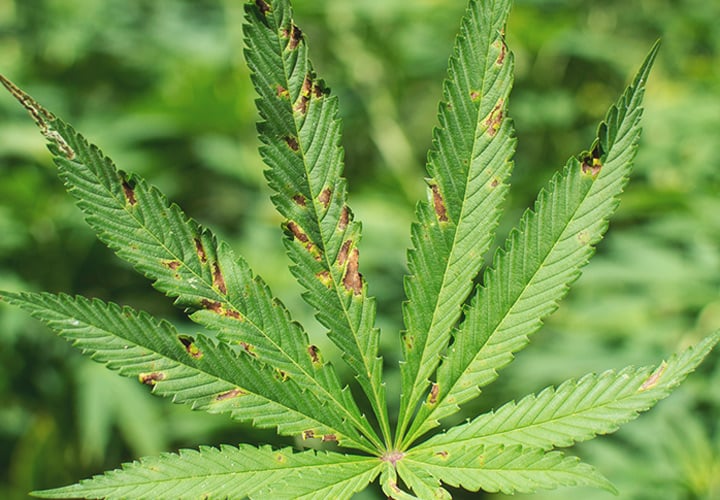


12. Incorrect pH Level
Incorrect pH level of your nutrient solution is among the most common reasons for cannabis growing problems, including slow growth. The reason for this is that cannabis thrives only in a relatively small window of suitable pH values. If the pH is off, the plants are unable to take in nutrients, even if they are present.
Make sure to dial in the correct pH level depending on your growing method. If you grow in soil, make sure the pH level is from 6.5 to 7.0. If you grow in hydro, an optimal pH level is 5.6 to 5.8. For soilless grows, such as coco, a pH level of 6.0 to 6.3 is optimal.
13. Temperatures Are Too Low or Too High
Cannabis likes it warm to grow healthy, and does best at daytime temperatures between 25–30°C. Temperatures lower than that will slow down your plant’s metabolism, resulting in slower growth. But excessive temperatures are not optimal either. At very high temperatures, heat stress can also slow down or even halt plant growth altogether. If you grow indoors, adjust your temperature to a comfortable level. You can also provide some cooling with fans that blow a mild stream of air over your plants. This can also help prevent hot air pockets from forming inside your grow room.
14. Planting Pots Are Too Big
Cannabis growers often start their seedlings in small cups. Later on, when the plants have reached an adequate size, they will “pot-up” to larger containers.
If you start your cannabis plants in containers that are too big, there is a high risk that you’ll overwater them. The issue is that seedlings cannot absorb all the moisture that is held in a large container, unlike mature cannabis, which can “drink” much more. Furthermore, a large pot will also take much longer to dry out.
To avoid the problems that come with too much soil and moisture, start seedlings in smaller containers until they’re growing vigorously. Once they have a set of 5–6 real leaves (not counting the cotyledons), then transfer them to a larger container, at least twice the current size.
If your seedling is already in a big container and you don’t want to or can’t move it into a smaller cup, water only a small area around the seedling.
What Is The Right Size Pot For Your Cannabis Plant?
Use this rough guide to determine what size pot you should use for your cannabis plant:
- Plant height 30cm: 7.5–11l container
- Plant height 60cm: 11–19l container
- Plant height 90cm: 18–26l container
- Plant height 120cm: 22–37l container
- Plant height 150cm: 30–37l+ container
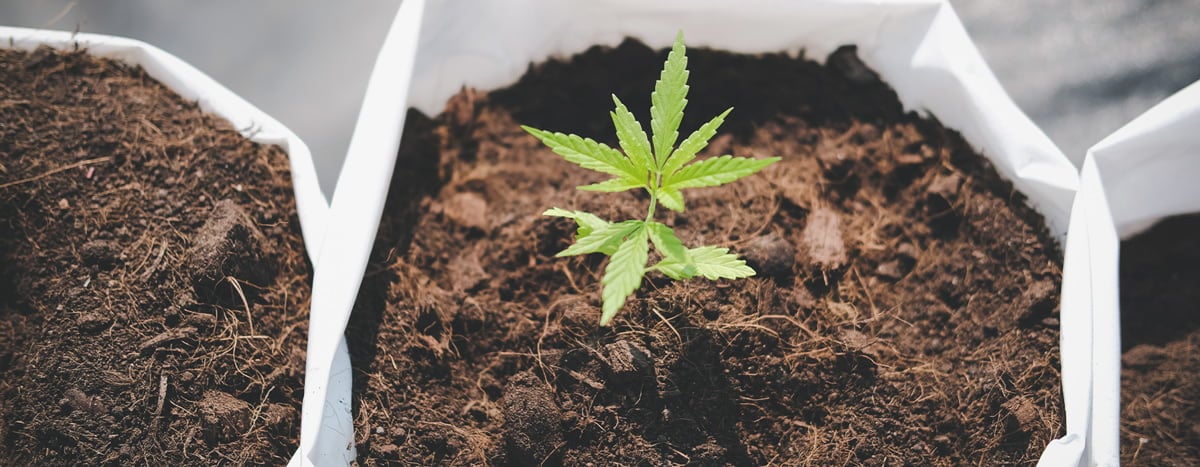
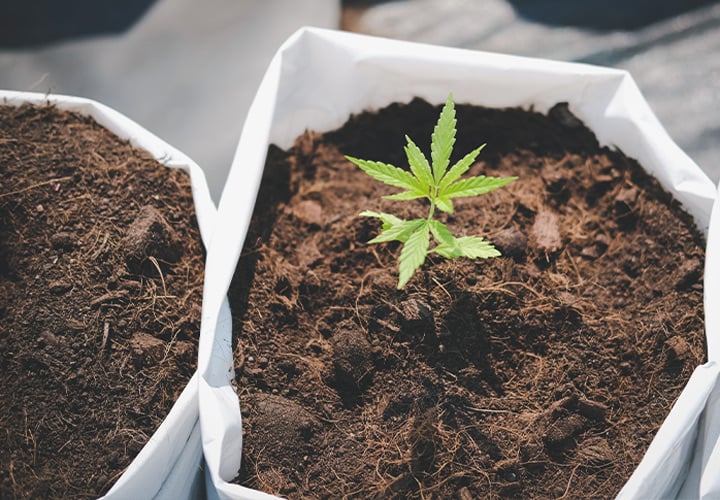


15. Stress Caused by Pests / Diseases
Insects, pests, and disease can cause damage and compromise a plant’s immune system. In a best case scenario, your plant may survive, but you will have poor yields. In the worst case, your plants could die.
Insects may feed on the leaves, affecting a plant’s ability to retain water and transpire. Other pests may damage the roots or cause additional problems. Any time your plant is sick or infested with insects, it will spend most of its energy defending itself and recovering from damage, which will slow down growth.
If your plants are infested, you’ll want to treat them immediately with appropriate measures. Even better, you can use preventative methods (e.g. neem oil, slug barriers, etc.) to minimise the risk for pest infestations. During all stages of growth, ensure that you regularly check for symptoms of pest infestations, including under the leaves.
16. Stress Caused by Tissue Damage
Physical damage, such as broken branches, can significantly slow your plant’s growth. Any damage will make the plant redirect valuable resources to repair wounds—resources that could be better spent on growing or flower production.
If you’re growing outdoors, situate your plants in an area sheltered from strong winds and heavy rains, and use chicken wire and stakes to maintain support.
Seedlings and young cannabis plants are especially vulnerable. Allow your seedlings to mature indoors for some weeks before setting them outside.
17. Stress From Cannabis Training Techniques
Tissue damage from high-stress plant training techniques always causes some delay in plant development. But when you’re pruning excessively or too frequently, your plant may ultimately spend more energy repairing itself than growing.
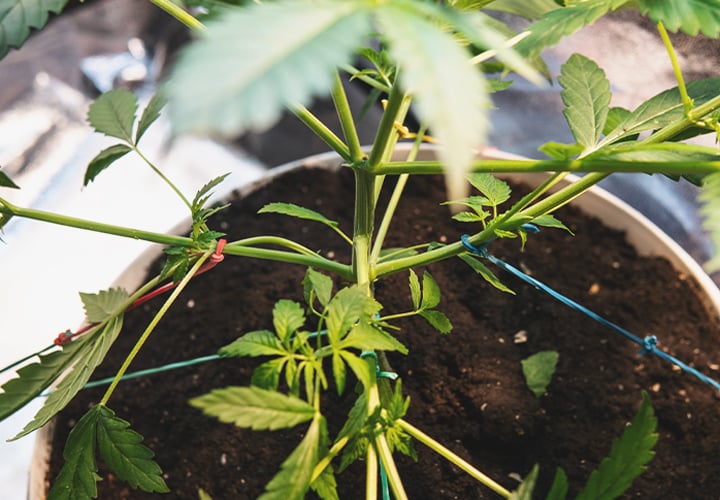


If you plan on pruning, don’t overdo it. Be aware that each pruning can delay the development of your plant for days, if not weeks.
If you’re using other plant training techniques such as topping, make sure you start as early as possible. If you’re growing autoflowers, don’t use any plant training techniques that involve tissue damage, such as pruning and cutting.
18. Age Stress
Older cannabis plants have different nutritional requirements than young plants. Their tissues become hard and woody, they’re less vigorous, and they're unable to take in as many nutrients.
Because of this, you’ll want to adjust your feeding regimen accordingly. Otherwise you risk overfeeding, which in turn results in stunted growth, deficiencies, and disease. Keep this in mind if you’re keeping mother plants around for a long time.
 Grow Guide Topic Finder
Grow Guide Topic Finder
- Growing cannabis step by step
- Cannabis growing basics
- Choosing your seeds
- How to germinate seeds
- The cannabis vegetative stage
- The cannabis flowering stage
- Harvesting cannabis
- Trimming, drying, and curing
- Choosing pots and soil
-
Growing indoors
- A Complete Overview Of Growing Cannabis Indoors
- Cannabis Cultivation Tips: How To Set Up Indoor Grow Lights
- How Many Cannabis Plants Can You Grow Per Square Metre?
- Indoor Cannabis Growing: Relative Humidity and Temperatures
- Hydroponics Cannabis Growing Guide (with diagrams)
- Cannabis Micro Growing: Growing Great Weed in Tiny Spaces
- Growing outdoors
- How to grow autoflowering cannabis
- Cannabis nutrients and pH
- Cannabis troubleshooting: Nutrients
-
Cannabis troubleshooting: Growing
- Cannabis Seed Germination — Troubleshooting Guide
- How to Deal With Pythium (Root Rot) in Cannabis Plants
- Slow Cannabis Plant Growth And What You Can Do About It
- How to Deal With Leggy Cannabis Seedlings
- Watering Your Cannabis: How to Fix Overwatering and Underwatering
- Understanding Male, Female, And Hermaphrodite Cannabis
- Identifying and Treating Common Cannabis Ailments
- How To Revive a Sick Cannabis Plant
- How to Avoid Mouldy Weed During Drying and Curing
- How to Prevent and Treat Dry and Crispy Cannabis Leaves
- What Cannabis Leaves Can Tell You
- Causes and Solutions for Yellow Cannabis Leaves
-
Cannabis Strains Grow Report
- HulkBerry Automatic Grow Report
- Blue Cheese Auto Grow Report
- Purple Punch Automatic Strain Grow Report
- Triple G Automatic Grow Report
- Do-Si-Dos Automatic Grow Report
- Green Gelato Automatic Grow Report
- Haze Berry Automatic Grow Report
- Purple Queen Automatic Grow Report
- Cookies Gelato Automatic Grow Report
- Sherbet Queen Automatic Grow Report
- Sweet Skunk Automatic Grow Report
- Medusa F1 Grow Report
- Cannabis plant training
-
Weed growing tips
- The Cannabis Plant Anatomy
- How to preserve seeds
- How Much Sunlight Do Outdoor Cannabis Plants Need To Grow?
- How to Control and Prevent Stretching in Cannabis Plants
- My Cannabis Plants Are Growing Too Tall: What Should I Do?
- Should You Worry About Purple Or Red Cannabis Stems?
- What To Do When Your Indoor Cannabis Won’t Flower
- How To Protect Your Cannabis Plants From Heat Stress
- How To Tell If Your Female Cannabis Plant Has Been Pollinated
- Growing Medical Marijuana
- Bud Washing: How to Clean Your Weed
- Understanding Cannabis Yield per Plant