.

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) — Here's What You Need To Know
HHC is making huge waves in the cannabis community. But being so new to the market, there's a ton of misinformation surrounding HHC's effects, safety, legality, and more. In this article, we explore all there is to know about hexahydrocannabinol, an intriguing analogue of THC.
Contents:
Thanks to changing perceptions and legislation, our understanding of cannabis is growing immensely. It seems that not a day goes by without news of a discovery related to cannabis making national or international headlines.
One of the latest subjects generating hype is hexahydrocannabinol, or HHC. But what exactly is this cannabinoid, how is it made, and what effects does it have on the body? Keep reading to learn all of this, and much more.
What Is HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol)?
Hexahydrocannabinol, or HHC, is a cannabinoid found in tiny concentrations in hemp seeds and pollen. However, the HHC making headlines across the world isn't derived from either of these sources. Instead, it is made in a laboratory using natural cannabinoids or cannabis extract.
Hence, HHC is often described as a semi-synthetic cannabinoid; while it isn't made solely using synthetic agents (e.g. K2 or Spice), the HHC sold in certain parts of the US and elsewhere around the globe undergoes a fair amount of human processing and isn't naturally present in cannabis plants.
While HHC has only recently jolted the attention of the media, it is actually far from a new discovery. HHC was first synthesised in the US in 1944 by Roger Adams, who created the compound by adding hydrogen molecules to delta-9-THC—a process known as hydrogenation. Since then, HHC hasn’t received much attention; that is, until recently, when manufacturers started selling it as an alternative to THC.
How Is HHC Made?
There’s a lot of misinformation about how HHC is made, and many manufacturers are very anxious about revealing their processes for producing this cannabinoid. However, the basic principle all manufacturers use to create HHC is the above-mentioned hydrogenation.
The process involves mixing a cannabis extract rich in cannabinoids and other compounds with hydrogen gas in a pressurised container. The hydrogen then naturally breaks down the double carbon bonds in the cannabinoids, creating a rich, dark-golden oil known as HCO (hydrogenated cannabis oil).
In order to accelerate the hydrogenation process, manufacturers typically use catalysts to speed up the chemical reaction between the hydrogen gas and the natural cannabinoids. Common catalysts used for this purpose include nickel, platinum, palladium, and illidium.
Depending on whether the cannabis extract used at the beginning of the process was decarboxylated or not, HCO manufacturers are left with a substance rich in either hexahydrocannabinolic acid (HHCA), or HHC. This oil can then be further refined according to the criteria of the manufacturer.
It’s also important to note that HCO contains two types of HHC: 9R HHC, which naturally binds to cannabinoid receptors, and 9S HHC, which, due to its odd chemical structure, doesn’t have a high affinity for CB1 or CB2 receptors. The ratio of 9R to 9S HHC in retail products such as gummies or vape cartridges, for example, can therefore greatly affect a product's potency and effects. More information about potency can be found further below.
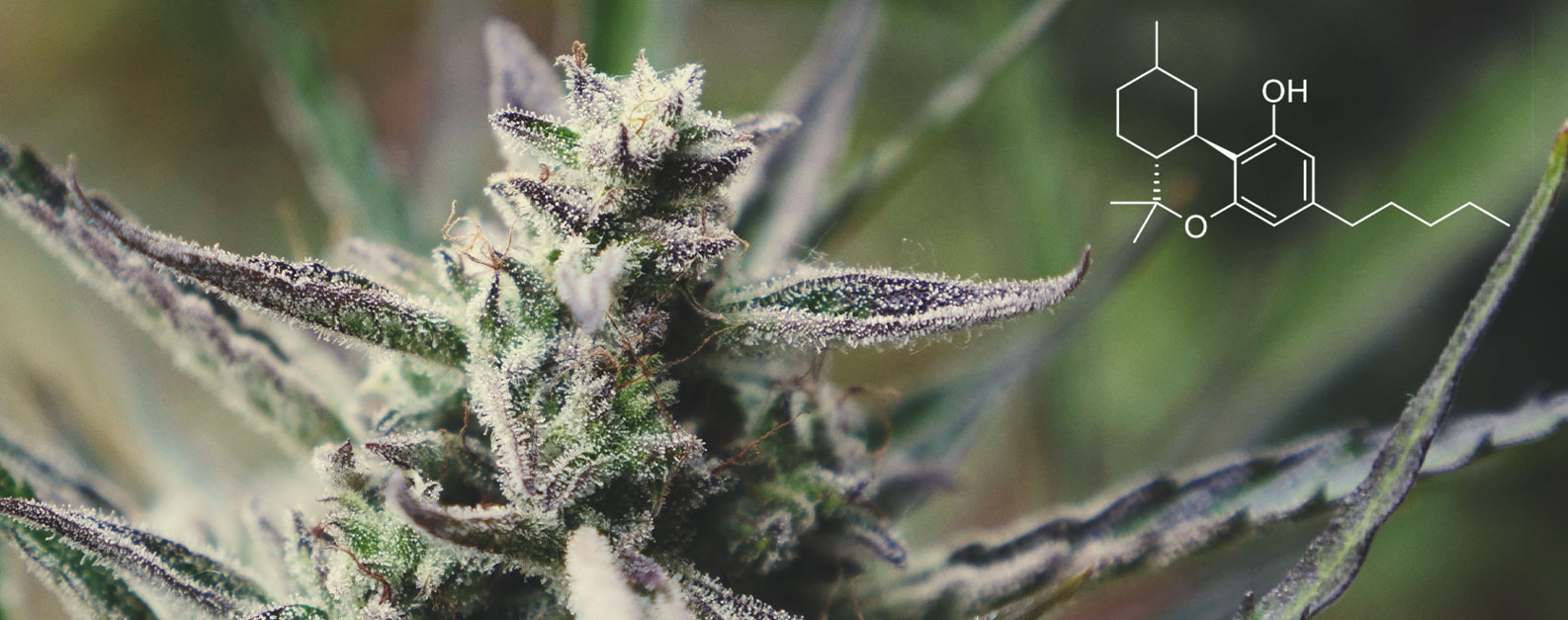
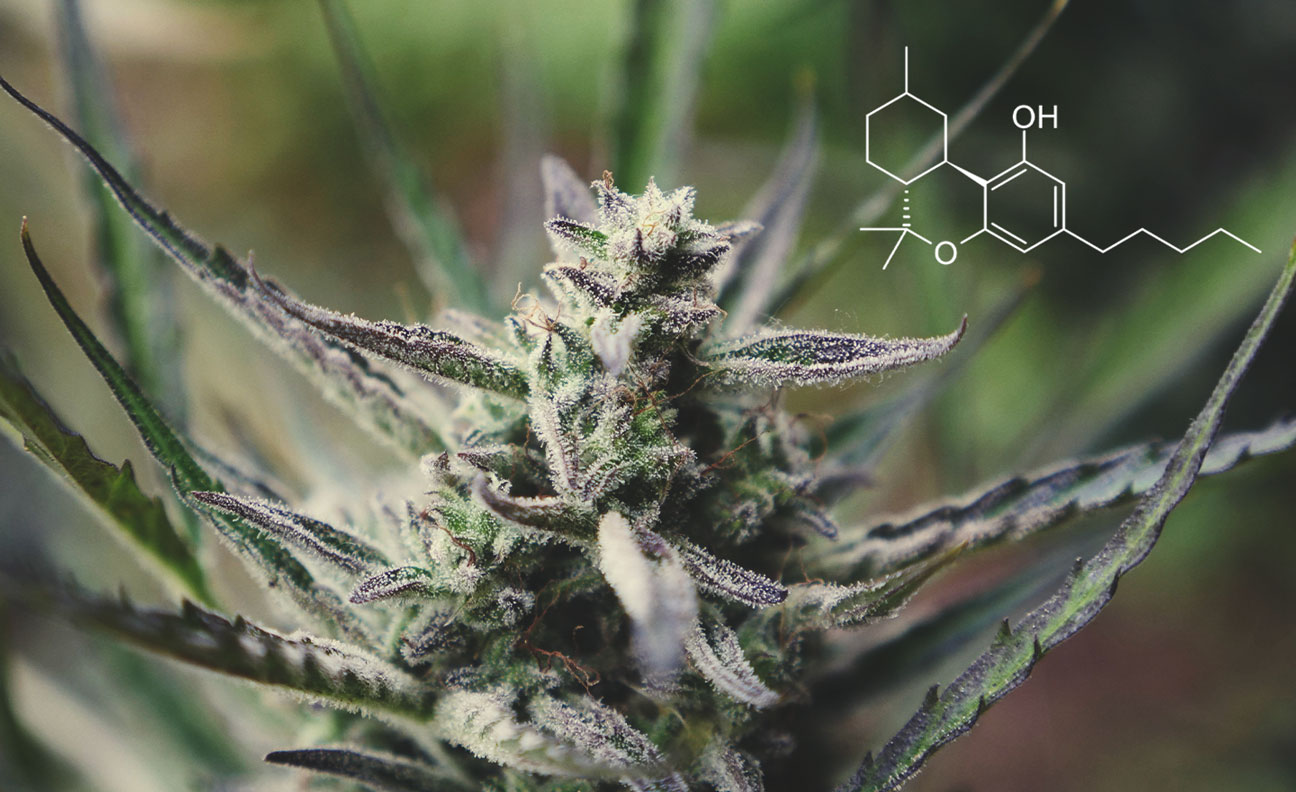


How Similar Are HHC and THC?
In terms of chemical structure, THC and HHC are very similar. The only notable difference between the two is that HHC has hydrogenated carbons, an extra carbon bond, and an ester atom.
According to Boston Hemp Inc[1], a retailer from Massachusetts selling CBD, delta-8-THC, and HHC products, these minor molecular differences make HHC a much more stable compound than THC. In turn, they claim that HHC products may be less susceptible to heat and light degradation, which could boost their shelf life.
HHC’s structural similarity to THC is likely what allows the compound to bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors (remember that cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors work in a lock-and-key fashion), and may also be why it produces effects similar to those of THC.
What Are the Supposed Effects of HHC?
HHC is so new to the market that most of the information available on its potential effects is anecdotal. Hence, you should take most of what you read about HHC with a very large grain of salt.
Manufacturers and retailers claim that HHC has a very high affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, and that by binding to these receptors, the compound delivers many of the same effects as THC, including:
| Euphoria | Altered mood |
| Laughter | Hunger |
| Changes in perception of reality | Increased sensory pleasure |
| Fatigue | Intoxication |
| Euphoria | Altered mood | Laughter | Hunger |
| Changes in perception of reality | Increased sensory pleasure | Fatigue | Intoxication |
How Potent Is HHC?
How HHC actually works in the body isn’t so straightforward. While it likely affects cannabinoid receptors, there is still a lot we don’t know about the cannabinoid’s potency, how to dose it correctly, whether it is as safe as other cannabis compounds, and more. Furthermore, different sources provide contradicting information about HHC’s properties and potency.
Some sources, for example, claim that HHC has roughly 70–80% the potency of delta-9-THC, which would make it roughly 20–30% more potent than delta-8 or delta-10. Others, however, claim that HHC is less potent than delta-8, and that high doses are needed for HHC to produce similar results to other types of THC.
As mentioned above, one potential reason for these contradictions is that different HHC products contain different ratios of 9R to 9S HHC, the former of which binds well to cannabinoid receptors, and the latter of which doesn’t. Therefore, products with higher concentrations of 9R HHC are likely to be perceived as more potent than those with higher concentrations of 9S HHC.
Is HHC Legal?
Manufacturers often tout HHC as a legal alternative to THC, seeing as it can be derived from delta-8-THC, which is typically found in high concentrations in hemp flowers. Retailers and HHC manufacturers also argue that HHC is legal because it is naturally present in cannabis pollen and hemp seeds, which therefore qualifies it as a natural hemp-derived extraction.
The reality, however, is much more complicated. The way cannabis is legislated varies greatly around the world and is subject to a lot of fine print. In the US, for example, some may argue that HHC is analogous to THC and is therefore subject to the Federal Analogue Act. If that were the case, HHC would, like THC, qualify as a Schedule 1 drug under US federal law.
Outside of the US, the laws governing HHC and similar cannabinoid alternatives can vary. In the EU, for example, there is no overarching law governing the control of cannabis across the union, and many European countries make exemptions for cannabis varieties containing low concentrations of THC (such as hemp). In these countries, HHC might technically be legal due to loopholes in the legislative system.
Does HHC Have Benefits?
Given its novelty (despite being discovered many decades ago), it is simply too early to come to conclusions about HHC's effects. The few hemp and cannabis retailers selling HHC products claim that they may have similar properties to THC-rich products, but there are no clinical trials or studies to back up any of these claims.
Is HHC Safe?
HHC retailers and manufacturers obviously advertise their products as safe and reliable. And to date, there have been no reports of HHC being toxic or producing negative effects. The truth is, however, that due to the lack of studies into HHC and its toxicology, we can’t make any claims regarding its safety.
HHC — The Bottom Line
HHC is a very new, semi-synthetic cannabinoid. And while it’s generating a lot of hype, and may prove to be an exciting and unique way to enjoy cannabis, we know very little about the compound and how it affects the body.
We recommend erring on the side of caution when experimenting with HHC, or any substance that hasn’t been studied extensively, until more information is available on its safety and effects profile.
- Boston Hemp Explains HHC And Its Effects https://www.prnewswire.com