.

Manganese Deficiency in Cannabis: Signs and Solutions
You know the importance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium when it comes to growing weed. You might know a thing or two about magnesium and calcium. But have you ever heard of manganese? This frequently ignored element exists outside of the limelight, but plays a critical role when it comes to growing good weed. Find out all about it.
Contents:
- Understanding the role of manganese in cannabis growth
- Cannabis and manganese deficiency: signs and symptoms
- The causes of manganese deficiency when growing weed
- How to treat manganese deficiency in cannabis plants
- How to prevent manganese deficiency when growing weed
- Manganese: a vital micronutrient for cannabis plant health
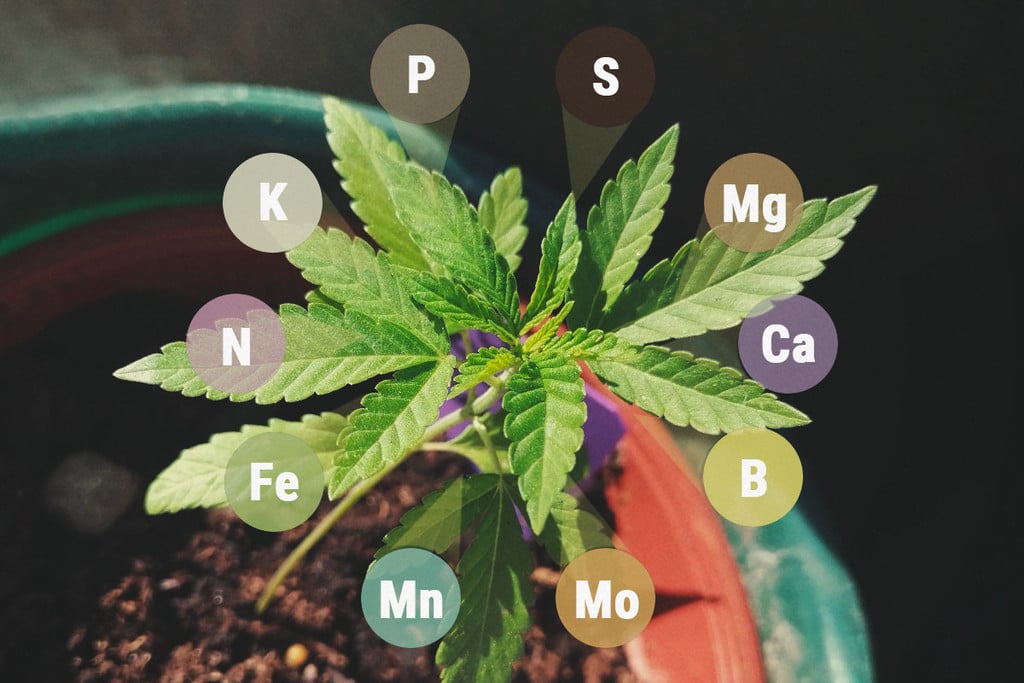
Cannabis plants require a palette of nutrients in order to flourish. Many growers focus almost entirely on nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to keep their plants well-fed; these are the three primary macronutrients, after all.
However, weed plants also need trace levels of certain micronutrients not only to thrive but to avoid the potentially catastrophic effects of deficiency. Manganese falls into this often-overlooked group. This element contributes to photosynthesis and facilitates important chemical reactions. Without enough, plants can quickly become stunted, yellow, and underproductive. Discover the signs of manganese deficiency and what you can do to fix it!
Understanding the Role of Manganese in Cannabis Growth
When it comes to growing healthy weed plants, there are a multitude of factors that growers need to consider. Alongside light and water, nutrients are crucial in helping plants to grow into virile and productive specimens. As the three primary macronutrients in plants, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium often receive the most thought. However, an array of key micronutrients also underpin cannabis plant health, including the likes of manganese.
Manganese: A Key Micronutrient For Cannabis
Manganese falls into the category of micronutrients. Unlike macronutrients, weed plants only require this nutrient in trace quantities. However, the reduced demand for these nutrients by no means minimises their importance. Without them, plants quickly exhibit signs of deficiency and performance takes a hit. Manganese remains somewhat overlooked even among plant micronutrients, but this element plays a critical role in plant physiology, from driving the water-splitting reaction that spurs photosynthesis to contributing to the oxidising process of respiration. Simply put, plants cannot reach optimal health and function without access to adequate amounts of manganese throughout the growing cycle.
The Function of Manganese in Cannabis Plants
You’re now aware of the general importance of manganese for weed plants. Before we delve into the signs of deficiency and how to correct them, let’s take a look at the specifics of manganese’s function in plant biology:
- Nitrogen metabolism: As one of the three macronutrients needed by plants, nitrogen forms the basis of amino acids and important proteins. Adequate levels of manganese help to support nitrogen metabolism in plants by stoking enzymatic processes and contributing to photosynthesis.
- Enzyme activation: Enzymes are large and complex proteins that help to catalyse chemical reactions in plant cells. Manganese works as a cofactor to several crucial enzymes, meaning it helps to activate them and preserve their structural integrity. Namely, it serves to activate superoxide dismutase, arginase, and pyruvate carboxylase.
- Respiration: This process involves the production of energy by way of plants combining the sugars created during photosynthesis with oxygen. Manganese helps to facilitate this process by acting as a cofactor for enzymes that are involved in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Also known as the Krebs cycle, this series of reactions produces energy from organic molecules.
Cannabis and Manganese Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms
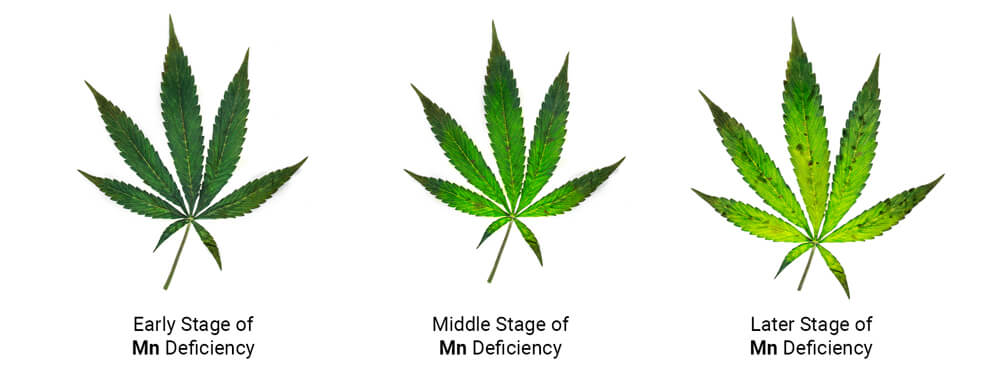
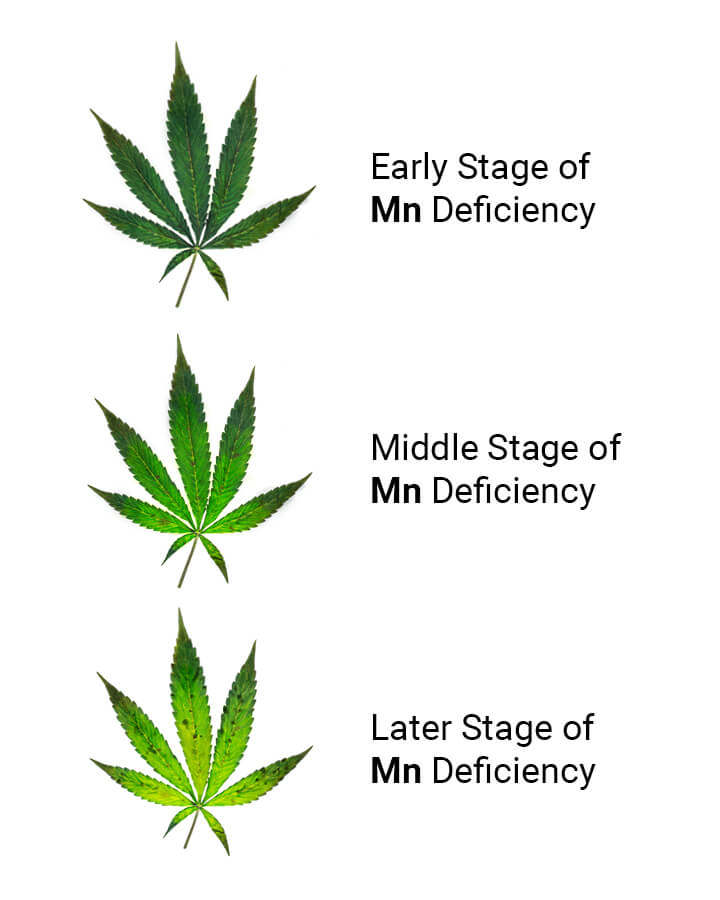
Any good cannabis deficiency chart will show you the changes in color and appearance that take place during cases of manganese deficiency. However, other symptoms occur that aren’t always present in these useful visual tools. Below, you’re going to discover everything you can expect to see when manganese deficiency rears its head.
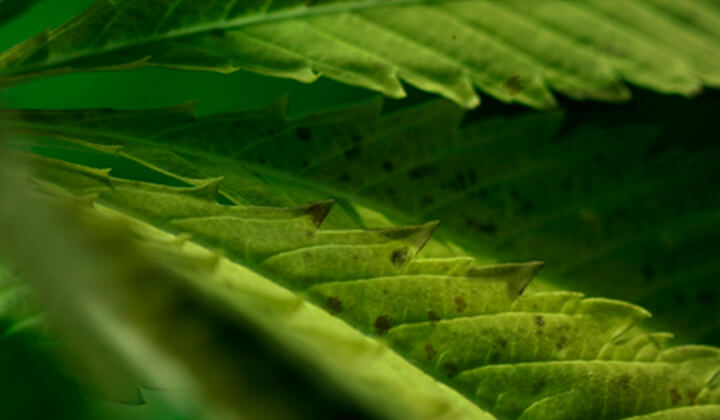


Chlorosis
Chlorosis refers to the loss of the normal green color of plant leaves. The chlorophyll pigment gives leaves their usual luscious appearance. A loss of this compound occurs in instances of manganese deficiency because this element, along with iron, contributes to the formation of chlorophyll molecules. Because this pigment helps to convert light into energy, a lack of it disrupts photosynthesis at the foundational level.
Interveinal Chlorosis
Diving deeper into plant anatomy, chlorosis that occurs in cases of manganese deficiency shows up chiefly within interveinal areas, that is, the pieces of tissue between the veins of the leaves. As these patches begin to lose their color, the tissue directly adjacent to the veins remains dark green, creating a stark contrast in color.
Distorted Leaf Structure
Manganese deficiency doesn’t just affect the color of leaves, it also takes a toll on their shape and structure. As the condition progresses, it causes malformed leaves that feature crinkled, curled, and wavy edges. This type of growth can affect the overall vitality and surface area of the leaf, reducing the ability of the structure to carry out effective photosynthesis.
Stunted Growth
As well as affecting leaf structure, a lack of manganese can also affect young shoots. If untreated, this can leave plants looking small, stunted, and unimpressive. After failing to form a strong and large canopy, plants ultimately possess fewer future bud sites, meaning productivity also takes a hit.
Poor Flower Development
Flower formation depends on several different factors, including gene expression and hormone production. However, blooming also requires energy. Because manganese plays an important role in photosynthesis, low levels can interrupt optimal flowering, resulting in smaller buds and lighter harvests.
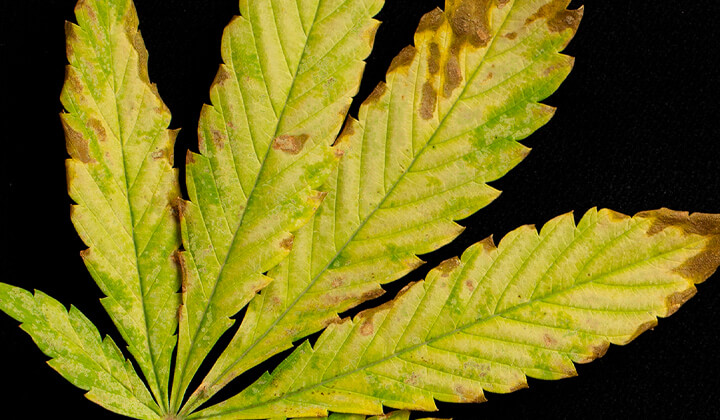
Necrosis
Necrosis refers to the death of previously living tissues. Manganese deficiency can cause brown[1] spots on leaves which signifies the death and decay of plant cells. As well as detracting from photosynthesis and overall leaf function, this cellular death can predispose leaf tissue to problematic pathogens that can start to affect nearby healthy cells.


The Causes of Manganese Deficiency When Growing Weed
You’re now aware of the importance of manganese when growing weed, as well as the key signs of deficiency. Next up, we’re going to explore why these symptoms begin to show up in the first place:
- Skewed pH: The amount of hydrogen ions in the soil, represented by the metric of pH, can influence manganese uptake. When pH levels dip too low or soar too high, plants fail to properly extract this nutrient from the soil.
- Excess soil drainage: Not enough soil drainage can cause water to pool, creating anaerobic conditions that restrict oxygen and spur disease. However, manganese becomes more available[2] in poor drainage conditions. You don’t want soil that drains too fast but equally don’t want pooling water that will suffocate roots.
- Low organic matter: Organic matter plays a key role in building healthy soil. As such, too little can increase the likelihood of manganese deficiency, especially when combined with factors such as coarse, sandy soil with a high pH. On the other hand, when the amount of organic matter in the soil is high, the soil pH need to be lower in order to prevent deficiency.
- Diseased or damaged roots: Root damage caused by pooling water, pests, and disease can inflict enough damage to impair nutrient uptake. Plant-parasitic nematodes and root rot pathogens are common causes of root damage that can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
_1.jpg)
.jpg)
How To Treat Manganese Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Manganese deficiency in cannabis can cause a host of problems, such as reducing plant vigour and thereby reducing the size of your stash at the end of the growing cycle. To stop this from happening, you need to become aware of the fast-acting steps you can take to quickly set things right. Discover how to treat manganese deficiency in cannabis plants below.
Apply a Foliar Spray
Foliar sprays are the fastest way to get nutrients into your plants when facing a deficiency. This method of administration capitalises on the small pores on leaf surfaces, known as stomata, to bypass roots and get nutrients directly into the vasculature of weed plants. Simply apply a manganese foliar product with a mister in accordance with product instructions.
Correct pH
Manganese uptake issues often occur when pH gets too high and edges towards the alkaline side of the spectrum. Cannabis plants thrive at a pH of around 6.0, where they have no problems uptaking the element. Use pH up and down products to rapidly alter the pH of your growing medium back to the optimal figure.
How To Prevent Manganese Deficiency When Growing Weed
Proficient growers can quickly remedy manganese deficiency when they spot the signs early. However, by the time symptoms emerge, your plant will have faced some physiological setbacks. This might manifest as only slight damage to a few leaves or the extremes of stunted growth and necrosis. Either way, working to prevent manganese deficiency will help you avoid running into these problems altogether, allowing your plants to thrive. Check out a handful of surefire ways to keep this deficiency at bay below.
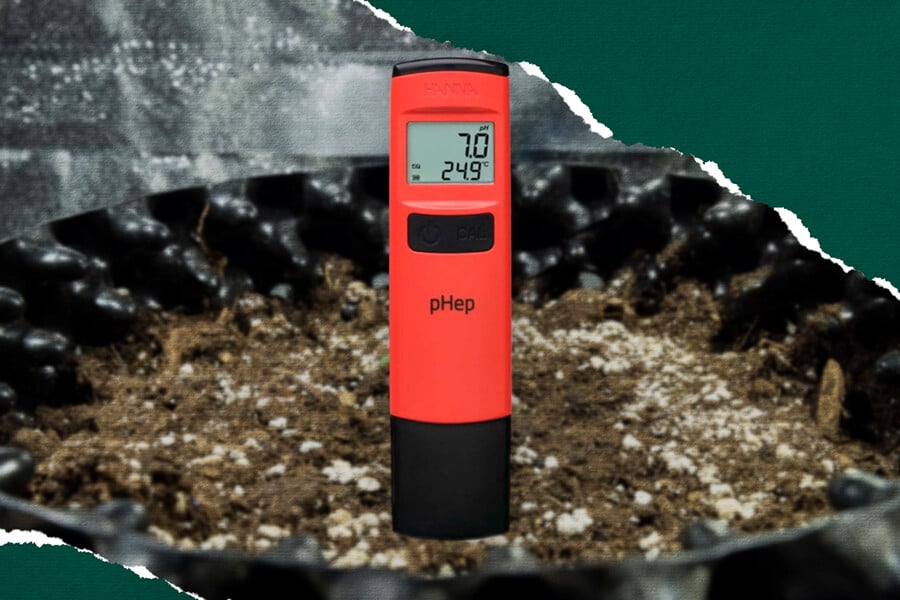
Frequently Measure Soil pH
Keeping on top of your soil pH will help you to prevent it from fluctuating too drastically. Maintaining a pH of around 6.0 will keep your plants in their sweet spot and prevent any obstructions to the uptake of nutrients. Aim to measure your runoff during watering around once per week through the entire growing cycle using a pH Tester. Modulate your pH, as and when needed, using pH up and down products. If you keep running into the same issues, opt for long-term organic methods to keep your pH where you want it.
Hit The Organic Matter Sweet Spot
Organic matter application has become a central tenet to growing among organic cultivators. Many aim to incorporate as much of this good stuff as possible by adhering to no-dig principles and layering on as much leaf mold, compost, and straw as they can get their hands on. However, applying too much organic matter can backfire by binding up key elements and restricting their mobility. If you’re facing this issue, routinely tilling your garden beds will help to liberate carbon and reduce organic matter levels over time.
Manganese: A Vital Micronutrient For Cannabis Plant Health
Your cannabis cultivation knowledge just improved substantially! You’re now much more familiar with one of the most under-looked cannabis nutrients. Although not well known, manganese serves a critical function within plant physiology; it contributes to photosynthesis and supports enzymes in completing important chemical reactions.
The symptoms of deficiency vary in severity from simple chlorosis all the way to stunted growth and even necrosis. You’re now aware of the causes of manganese deficiency in weed plants, and how to quickly correct it using foliar sprays and modulating pH. To prevent it from showing up again, you’re equipped with strategies for managing organic matter and monitoring soil pH.