.

Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis: Signs and Solutions
Phosphorus is a macronutrient that is necessary for the development of the cannabis plant. When phosphorus concentrations are lacking, problems can occur. Read along to find out how to identify, treat, and prevent phosphorus deficiency in your cannabis plants.
Feeding cannabis plants is an art unto itself. Too much or too little, and you can encounter serious problems. Here, we look at the roles that phosphorus plays in weed plants, and then how to spot, reverse, and prevent a deficiency.
Contents:
- Understanding the role of phosphorus in cannabis growth
- Cannabis and phosphorus deficiency: signs and symptoms
- The causes of phosphorus deficiency when growing weed
- How to treat phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants
- How to prevent phosphorus deficiency when growing marijuana
- Phosphorus: an important mineral from root to bud
Understanding the Role of Phosphorus in Cannabis Growth
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient that’s necessary for cannabis growth and development. Without it, you’ll find that your plant doesn’t get far at all. Understanding the role of phosphorus will help you to understand how best to apply it, and how to spot if your plant isn't getting enough.
Phosphorus: A Primary Macronutrient for Cannabis
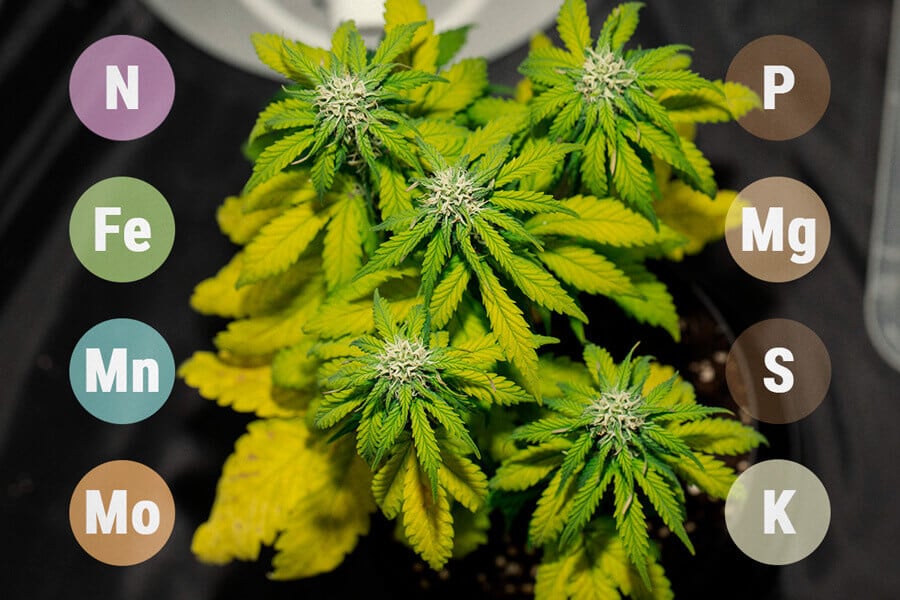
Phosphorus is, for cannabis, what’s known as a macronutrient. Macronutrients are those key nutrients that cannabis plants require in large quantities, and without which they simply can’t survive. There are three macronutrients for cannabis:
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
Together, these three macronutrients are expressed as an NPK ratio. This ratio is essential to understand as it can be found on practically all cannabis feeds. Without this information, feeding your plants will require a lot of guesswork.
The Function of Phosphorus in Cannabis Plants
In cannabis, phosphorus can be considered perhaps the second most important macronutrient, after nitrogen. Phosphorus plays the following roles in the cannabis plant:
- Energy transfer: Phosphorus helps to facilitate energy transfer within the plant, allowing it to carry out its essential functions.
- Photosynthesis: Without this macronutrient, photosynthesis wouldn’t be able to happen. Photosynthesis is the process whereby plants turn raw ingredients into sugars, which they use to grow.
- DNA and RNA synthesis: Continual DNA and RNA synthesis is necessary for organisms to produce new cells and to keep growing and developing.
- Root development: Especially in the earlier stages of growth, phosphorus facilitates root development, helping a plant to become strong.
- Flower and fruit formation: Phosphorus plays a key role in the development of cannabis flowers, and as such is needed in higher quantities in this last stage of growth.
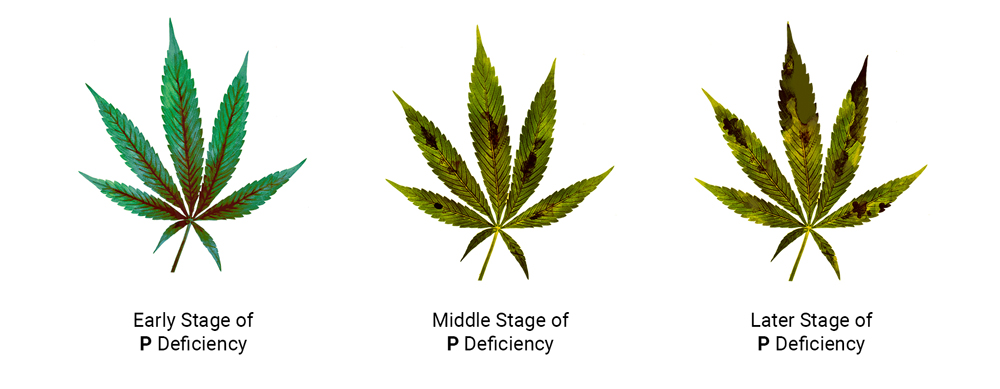
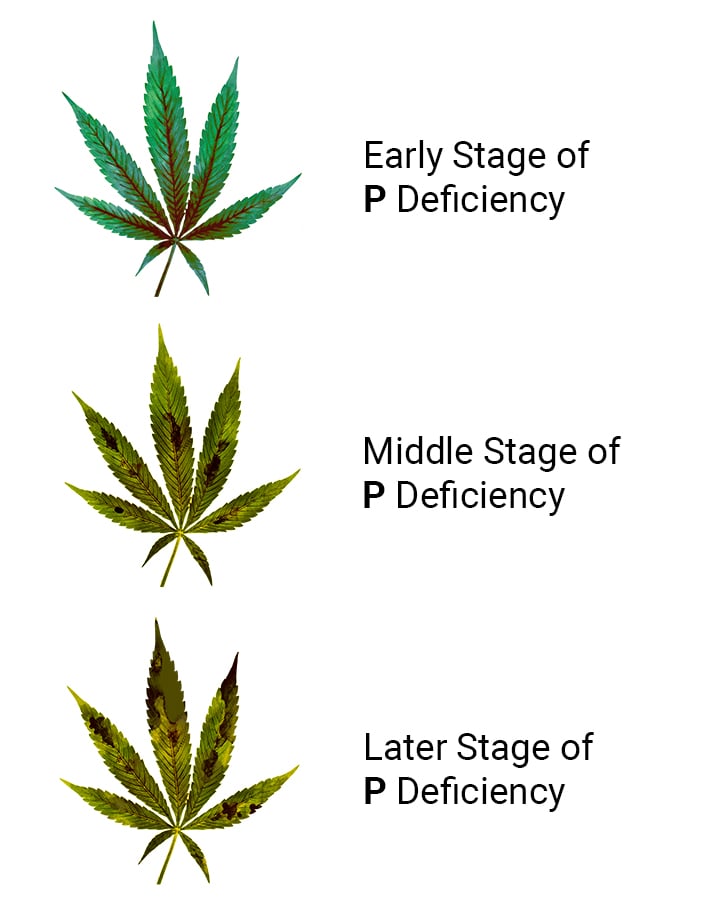
Cannabis and Phosphorus Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms
A phosphorus deficiency is fairly easy to spot and equally easy to solve. Identifying it early will prevent the issue from getting out of hand, and ensure that your plant returns to good health as soon as possible.


Stunted Growth
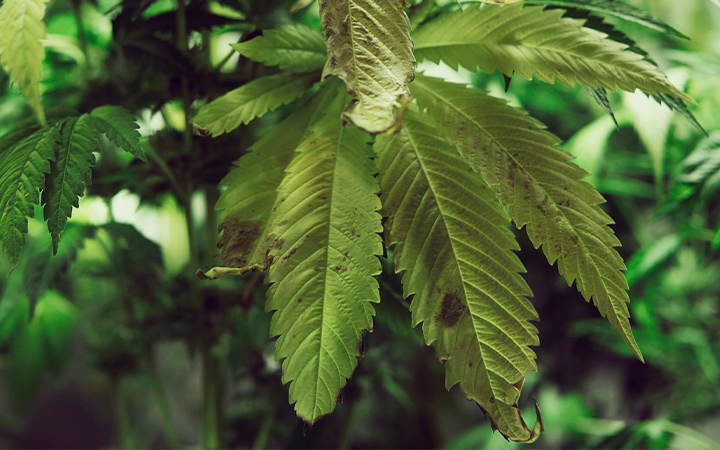
As phosphorus is so important, a plant will soon stop growing if it doesn’t have enough of it. In young vegetating plants, this will generally manifest as stalled vertical growth. In plants that are flowering, a phosphorus deficiency will be less obvious, but will show itself through meagre flower production.
Dark Green or Purple Leaves
At first, older leaves will take on a darker green colouration, before turning a blue/purple hue. This shouldn’t be mistaken for some cool purple phenotype. It’s one of the earliest signs of deficiency and should be dealt with. If untreated, then copper, burnt-looking patches will begin to appear.
Leaf Curling
Eventually, these burnt-looking leaves will begin to curl at the tips and edges. At this point, the phosphorus deficiency has progressed substantially, so try to prevent your plants from getting to this point.
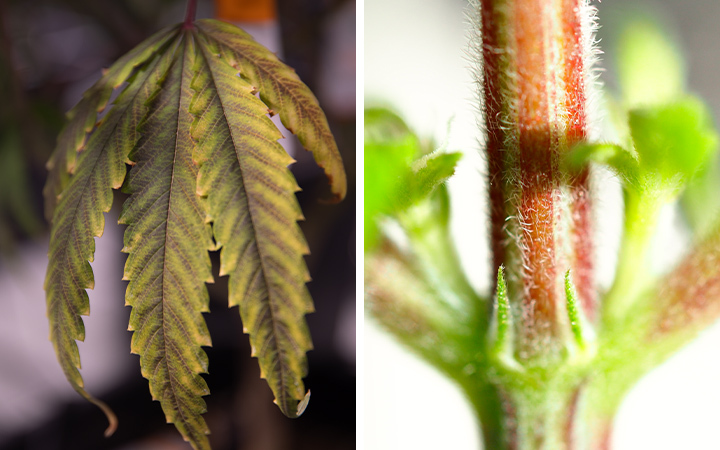


Red or Purple Stems
Alongside a change in leaf color, the colors of branches and stems can also change if there isn’t enough phosphorus present. They will likely take on a blue or purple, bruised-looking appearance.
Weak Stems and Branches
As cells degrade, the structure of your plant will weaken, and stems and branches will become more fragile. You might notice that they break easily, perhaps even snapping under the weight of their own flowers.
Lower Yields
Ultimately, if untreated, yields will suffer—sometimes greatly. Phosphorus is absolutely crucial for flower production, and a deficiency will certainly affect the final yield.
Reduced Resin Production
It isn’t just flower mass that’s negatively affected by a phosphorus deficiency, but resin production too. So not only will you have a smaller yield, but what you do harvest will be less potent too.
The Causes of Phosphorus Deficiency When Growing Weed
There are many potential causes of a phosphorus deficiency when growing cannabis, and familiarising yourself with these can help you to both prevent and treat it:
- Poor feeding regimen
- Perhaps the most likely cause is improper feeding. Maybe you’re using a low-quality feed, or perhaps you’re feeding too little. Alternatively, you could be feeding too often with synthetic nutrients and causing nutrient lockout (more on this shortly). Cannabis functions best when the right kind of nutrients are delivered at the right times.
- Lack of microbial life
- A lack of beneficial microbes, such as mycorrhizal fungi, can hamper your plants’ ability to uptake phosphorus and other nutrients. Your soil may lack life because it started off low quality, or because you’ve been putting poor-quality feed into it.
- pH imbalance
- A pH imbalance is another leading cause of phosphorus deficiency. Too high or too low, and a plant’s roots won’t be able to properly uptake phosphorus or other nutrients.
- Waterlogged soil
- Overwatered and soaked soil is not healthy for roots, and they will struggle in all manner of ways—and eventually die. Permanently drenched soil will cause a phosphorus deficiency alongside a host of other problems.
- Root damage or stress
- If the roots encounter problems, such as pathogens, the above-ground portions of the plant will also suffer.
How to Treat Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis Plants
Treating a phosphorus deficiency can be executed in multiple ways, and sometimes a multi-pronged approach is best. A word of caution though: don’t overdo it! Going overboard can seem like the best approach in the face of deficiency, but you’ll just create more problems.
Apply Ionic Nutrients as a Root Drench
Ionic nutrients are easily accessible to roots and can work as a rapid remedy. Due to their structure, plant roots can absorb them immediately, meaning you can return your plant to good health quickly.
These nutrients aren’t suitable for long-term use though, as they can easily cause overfeeding and damage the soil.
Apply a Phosphorus-Rich Foliar Spray
Foliar sprays are great for treating deficiencies, as they act fast and damage neither the soil nor the roots. They are applied directly to the leaves, where they are absorbed through tiny pores known as stomata. Results can be visible within as little as 48 hours from application.
Phosphorus-rich foliar sprays can include the likes of synthetic phosphorus, or, for an organic option, fish extract. Korean natural farming (KNF) is a holistic method of farming that takes inspiration from nature to improve plant growth and reduce the negative environmental impact of farming and horticulture. This practice uses fermented fruit juice (FFJ) to create nutritious foliar sprays.
Adjust Soil pH
If the pH of your substrate falls below 6.0 or rises above 7.0, then your plant’s roots are going to have a tough time absorbing ample amounts of phosphorus. If you spot a deficiency, measure your soil or runoff with a pH meter. If it’s outside of this range, then treat it with a pH up/down solution. These can be bought, or made from acidic/alkaline ingredients. Then, simply water your substrate with the appropriate solution until the runoff measures within the correct pH range.
How to Prevent Phosphorus Deficiency When Growing Marijuana
When planning and carrying out a grow, you should seek to feed your plants properly and prevent deficiencies in the first place—as you’ll save yourself lots of trouble.
Here’s how to keep things as they should be and prevent a phosphorus deficiency.
Improve Your Soil Biology
As mentioned, beneficial microbes in the rhizosphere (the region surrounding plant roots) can make a huge difference when it comes to how your plants absorb nutrients. Mycorrhizal fungi form a symbiotic relation with roots and, in exchange for sugars, absorb nutrients from the soil, delivering them to plants in an easy-to-use form.
Amending soil with such microbes will have a whole swathe of benefits, including better nutrient uptake and reduced chance of infection. Silicon is thought to be beneficial for mycorrhizal fungi, and thereby may further improve the rate of phosphorus uptake for cannabis plants. If you can, add it to your soil.
Refine Your Feeding Regimen
Honing in feeding is one of the best ways to prevent overfeeding. Primarily, this means following the instructions on the packaging correctly. But as you get deeper into cultivation, you may move away from premade fertiliser, or seek to supplement basic feeding with other methods.
These include organic methods (both commercial and homemade) and additional methods, such as using a fermented fruit juice foliar spray to regularly top up your plants with nutrients without the risk of causing nutrient lockout or damaging the rhizosphere.
Frequently Measure Soil pH
It’s good cultivation practice to regularly check the soil pH, as all sorts of things can go awry if this gets thrown out of balance. You can easily check the pH of your soil and feed using a pH meter. Measure the runoff as it comes out of the bottom of your pots to ensure you’re within the appropriate range (6–7 in soil).
As mentioned, if your pH is ever outside of these ranges, use dedicated pH up and down products to bring it back into the desired range.
Make Your Own Compost
Making your own compost is a great way to feed your plants a steady supply of organic, highly fertile feed. Compost is rich in both organic nutrients and beneficial microbes—both of which will stave off nutrient deficiencies.
Lay Off the Synthetic Fertiliser
Synthetic fertilisers, while helpful in an emergency, are generally best avoided. Once popular, it is now known that these tend to do more harm than good.
First, it’s easy to overfeed with them, which can also stop your plants from absorbing nutrients and can be a hassle to sort out. Second, they destroy the soil microbiome and suppress the action of beneficial microbes, which at once reduces a plant’s ability to absorb nutrients and increases the chances of disease.


Phosphorus: An Important Mineral From Root to Bud
A phosphorus deficiency will show itself first as reduced growth and a slight discoloration on the leaves, and will develop into leaf curling and severely reduced growth and yields. If spotted early, you can easily reverse it using one of the methods listed above. The good news is that it’s easy to treat. And if you act fast, there’s no lasting bad news!