Everything you Need to Know About CBD (Cannabidiol)
It's time to focus on CBD, the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana. Despite being less well-known, CBD could have a significant impact on well-being. Keep reading to find out what you need to know about this important compound.
Your definitive guide to CBD, the lesser-known cannabinoid with a significant impact.
Contents:
- What is cbd?
- Does cbd come from hemp or cannabis?
- How does cbd work?
- Cannabinoid mechanisms of action
- Different types of cbd extracts: isolate, broad spectrum, and full spectrum
- Cbd:thc ratio
- What are the effects of cbd?
- Does cbd have any side effects?
- Methods of consuming cbd
- Different carrier oils for cbd
- What does cbd oil taste like?
- How to dose cbd
- Cbd for pets
- Is cbd legal?
Take a look inside the Cannabis sativa species, and you'll see a rich and diverse collection of chemical compounds. Some of these compounds we know very well, such as the iconic, high-inducing THC. But, there’s also the lesser-known cannabinoid, CBD, to consider. Why? Because CBD has several qualities that THC simply doesn't provide.
What Is CBD?
Both CBD and THC belong to a vast family of compounds (an estimated 113 in total), with each cannabinoid interacting slightly differently with the human body. And, although our knowledge is limited regarding the other cannabinoids, we're slowly learning more about the second most abundant one and the focus of this article—cannabidiol (CBD).
CBD is like a brother or sister to THC, but it doesn’t share the psychoactive properties of the latter. In other words, it won't induce a high like THC. The two compounds do, however, share a similarity.
Does CBD Come From Hemp or Cannabis?
While the answer is technically both, the highest concentrations of CBD come from hemp, a subspecies of Cannabis sativa favored by commercial industries. Thanks to modern breeding, and a touch of natural selection, hemp has a chemical structure rich in CBD and low in THC.
And, although hemp is the plant of choice when it comes to consumer products such as CBD oil, CBD supplements, and CBD cosmetics, cannabis isn't entirely out of the game. You'll just need to pick varieties bred specifically for their CBD content.
In fact, it is the cannabis industry’s quest for CBD-rich strains that has triggered somewhat of a revolution, especially in the last twenty years. High-CBD strains are finally becoming commonplace, the direct result of diligent breeders, and their manipulation of strains with CBD-dominant phenotypes.
For home growers, there’s no need to worry about crossing cannabis strains, or cloning mother plants rich in CBD. Instead, seed banks offer an abundance of choice. For example, RQS’ selection of CBD cannabis strains includes Solomatic, Purplematic and Joanne’s CBD, a strain high in CBD with almost no THC.
But, as we’ll find out, creating CBD-dominant strains isn’t as straightforward as it sounds. With cannabis, it always comes back to genetics. It's a plant's genetics that dictates how long it takes to flower, its resistance to disease. These genetics also control the cannabinoids and terpenes within.

The Importance of Genetics
During the earliest stages of a plant's development, the ratio of cannabinoids is determined by biosynthesis of the cannabinoid precursor CBGA with a selection of enzymes. However, it can't bind with all three, and depending on which one CBGA binds with, determines whether a strain is CBD or THC dominant (or a mix of both).
However, as we've highlighted, cannabis plants are strictly controlled by their genetics. So, once nature has done the hard work for you, it's possible to cross similar CBD strains, or clone a mother plant, refining the concentration with every iteration.
Over the years, breeders have worked to perfect the process outlined above, selecting strains that display the correct phenotypes. Of course, there's still an incredible amount of experimentation taking place, but the number of CBD-dominant cannabis strains has already increased dramatically. It's also through manipulation of various CBD phenotypes that breeders can alter the ratio of cannabinoids inside cannabis, a subject we'll cover in more detail shortly.
But, getting hold of CBD is only part of one piece of the puzzle. To understand why this cannabinoid deserves your attention, we also need to know how it interacts with the body.
How Does CBD Work?
All cannabinoids work via a unique interaction with our endocannabinoid system (ECS). This vast network of receptors exists inside all of us, and is responsible for maintaining a balanced state. When our biological systems are balanced, our body is better equipped to deal with disease, disorder and the challenges of modern living.
To activate the ECS, cannabinoids bind with cannabinoid receptors (split into CB1 and CB2) located on cells throughout our body.
These receptors act as gatekeepers, proteins embedded in cells that direct chemical signals, telling them what to do and when to do it. However, they don't just act of their own accord. The action CB receptors take depends on their location in the body and the interacting cannabinoid.
Receptors are particular when it comes to which cannabinoids they bind with. The mechanism is like a lock and key—receptors only activate if they detect a cannabinoid with the right shape to match their lock. It's via these access points that cannabinoids can influence the body in a variety of ways.
The majority of CB1 receptors exist in the brain, digestive, and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are prevalent in our immune system. THC, for example, activates CB1 receptors responsible for balancing mood and motivation, hence the euphoric high. CBD, on the other hand, takes a less direct approach, as we'll discover.
Cannabinoid Mechanisms of Action
Disclaimer: These findings are based upon ongoing pre-clinical and clinical investigations. Many of these mechanisms have only been identified in cell and animal models, and are not the results of controlled human clinical trials. These results do not necessarily reflect how cannabinoids work in the human body.
|
THC-A
|
THC
|
THC-V
|
CBN
|
CBD-A
|
CBD
|
CBC-A
|
CBC
|
CBG-A
|
CBG
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analgesic Pain relief |
THC | CBN | CBD | CBC | ||||||
| Anti-inflamatory Reduces inflamation |
THC-A | CBD-A | CBD | CBC | CBG-A | CBG | ||||
| Anorectic Suppresses appettite |
THC-V | |||||||||
| Appetite stimulant Stimulates appetite |
THC | CBD | ||||||||
| Antiemetic Reduces vomiting and nausea |
CBD | |||||||||
| Intestinal anti-prokinetic Reduces contractions in the small intestine |
CBD | |||||||||
| Anxiolytic Relieves anxiety |
CBD | |||||||||
| Antipsychotic Tranquilizing, used to manage psychosis |
CBD | |||||||||
| Antiepileptic Reduces seizures and convulsions |
THC-A | THC-V | CBD | |||||||
| Antispasmodic Supresses muscle spasms |
THC | CBN | CBD | |||||||
| Anti-insomnia Aides sleep |
CBN | CBD | ||||||||
| Immunosuppresive Weakens the inmune system |
CBD | |||||||||
| Anti-diabetic Reduces blood sugar levels |
THC-V | CBD | ||||||||
| Neuroprotective Prevents nervous system degeneration |
CBD | |||||||||
| Antipsioriatic Treats psoriasis |
CBD | |||||||||
| Anti-ischemic Reduces risk of artery blockage |
CBD | |||||||||
| Anti-bacterial Kills or slows bacteria growth |
CBD | CBC-A | CBC | CBG | ||||||
| Anti-fungal Treats fungi infection |
CBC-A | CBG | ||||||||
| Anti-proliferative Could inhibits cell growth in tumors/cancer cells |
THC-A | CBD-A | CBD | CBC | CBG | |||||
| Bone stimulant Promotes bone growth |
THC-V | CBD | CBC | CBG |
|
THC-A
|
THC
|
THC-V
|
CBN
|
CBD-A
|
CBD
|
CBC-A
|
CBC
|
CBG-A
|
CBG
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analgesis Pain relief |
THC
|
CBN
|
CBD
|
CBC
|
||||||
| Anti-inflamatory Reduces inflamation |
THC-A
|
CBD-A
|
CBD
|
CBC
|
CBG-A
|
CBG
|
||||
| Anoretic Suppresses appettite |
THC-V
|
|||||||||
| Appetite stimulant Stimulates appetite |
THC
|
CBD
|
||||||||
| Antiemetic Reduces vomiting and nausea |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Intestinal anti-prokinetic Reduces contractions in the small intestine |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Anixolytic Relieves anxiety |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Antipsychotic Tranquilizing, used to manage psychosis |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Antiepileptic Reduces seizures and convulsions |
THC-A
|
THC-V
|
CBD
|
|||||||
| Antispasmodic Supresses muscle spasms |
THC
|
CBN
|
CBD
|
|||||||
| Anti-insomnia Aides sleep |
CBN
|
CBD
|
||||||||
| Immunosuppresive Reduces the efficacy of inmune system |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Anti-diabetic Reduces blood sugar levels |
THC-V
|
CBD
|
||||||||
| Neuroprotective Prevents nervous system degeneration |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Antipsioriatic Treats psoriasis |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Anti-ischemic Reduces risk of artery blockage |
CBD
|
|||||||||
| Anti-bacterial Kills or slows bacteria growth |
CBD
|
CBC-A
|
CBC
|
CBG
|
||||||
| Anti-fungal Treats fungi infection |
CBC-A
|
CBG
|
||||||||
| Anti-proliferative Inhibits cell growth in tumors/cancer cells |
THC-A
|
CBD-A
|
CBD
|
CBC
|
CBG
|
|||||
| Bone stimulant Promotes bone growth |
THC-V
|
CBD
|
CBC
|
CBG
|
CBD and the Endocannabinoid System
Although we said all cannabinoids interact with the human body via a lock and key mechanism, CBD's interaction is a little more complicated.
Cannabidiol does not have much binding affinity to either of the two known cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it exerts its influence by supporting the entire ECS, improving how the system operates and regulating the production of beneficial enzymes.
It's believed to have a suppressive effect on the enzyme FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) which is a molecule responsible for breaking down and destroying anandamide (AEA).
This suppressive reaction with CBD means that more anandamide will stay in your system, and for extended periods too. This matters because AEA is an internally produced chemical that exerts a positive influence on eating, sleeping, pain relief, and more.
But, while CBD doesn't care to bind with CB1 or CB2 receptors, that doesn't mean it completely bypasses the lock and key mechanism we highlighted earlier. There are a handful of G-protein receptors located in the central and peripheral nervous systems that interact with CBD. There is also the TRPV-1 (transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V-1) that reacts to CBD. The TRPV-1 receptor is known to mediate pain perception, inflammation and body temperature, but the potential of this interaction remains under investigation.
The Entourage Effect
So far we've covered how cannabinoids exert their influence, and how CBD takes a slightly different approach via its impact on enzymes and niche receptors. What we haven't discussed, however, is their collaboration.
Although THC and CBD have very different effects and interaction methods, there is one characteristic they share. When they work together, their respective abilities are enhanced. In fact, the entourage effect is a phenomenon that, theoretically, applies to all cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids.
Cannabis researchers such as Dr Ethan Russo are exploring the idea of synergy between different cannabis constituents, including cannabinoids and terpenes. The chemical complexity of full-spectrum products certainly offers a different experience compared to isolates.
Different Types of CBD Extracts: Isolate, Broad Spectrum, and Full Spectrum
When it comes to CBD products that are made via extraction—oil, vape juice, gummies—the specific extraction and post-extraction processes will influence which compounds make it into the final product. This in turn determines whether the product could be thought to offer an entourage effect.
CBD Isolate
If a product is deemed a CBD isolate, then the only cannabis compound it contains is CBD, potentially with trace levels of terpenes. The extraction process isolates CBD, which is then stored in a carrier oil for use. As CBD isolates lack the accompanying compounds found in the cannabis plant, they do not offer an entourage effect.
Broad-Spectrum CBD
Broad-spectrum CBD contains a range of compounds from cannabis flowers, but not all of them. Specifically, broad-spectrum products tend to include essentially the entire cannabis phytocomplex, except for THC. Depending on the exact selection of compounds in a broad-spectrum CBD product, its potential entourage effect will vary.
Full-Spectrum CBD
Full-spectrum CBD products contain all of the compounds found in a raw plant’s flowers. As the name suggests, everything is extracted and deposited into a carrier. These products will contain CBD, very low levels of THC, other cannabinoids in the raw flower, as well as terpenes and flavonoids. Given this, many people consider full-spectrum CBD products to offer the most profound entourage effect.

CBD:THC Ratio
The interaction between CBD and THC is a phenomenon that's caught the eye of breeders and cannabis lovers alike. Why? Because it's possible to alter your high by adjusting the ratio of CBD and THC you’re taking in, gaining benefits from both cannabinoids.
Maybe you want a strain you can smoke throughout the day that won't dampen productivity or motivation. Thanks to advancements in cannabis breeding, it's entirely possible to find that ideal flower. For those with a lot on their plate, strains that feature high levels of CBD and minimal levels of THC (25: 1) fit the bill perfectly. You'll still gain the advantages of the entourage effect, but the experience is devoid of any psychotropic side effects.


However, keep tweaking the ratio of CBD and THC, and you can explore a whole other set of effects. A ratio of 8:1 or 2:1, naturally, will deliver a much stronger hit of THC. You’ll end up feeling the euphoric effects, and there’ll be some psychotropic sensations, but CBD being the dominant force helps balance the overall high.
Finally, you have cannabis strains with equal parts CBD and THC. While we recommend these for those well versed in the effects of THC, it's the ultimate combo of two cannabinoids with a powerful influence over the ECS. By consuming both in equal measure, your well-being benefits equally too—it's all about balancing the ratio of CBD and THC to your needs.
Royal Queen Seeds has an exclusive range of CBD cannabis seeds, each specifically bred to contain higher than usual CBD levels, and a balanced ratio of THC and CBD. Tatanka Pure CBD, for example, has between 9-14% CBD, which is much more than the typical cannabis strain. With several feminised and autoflowering high-CBD strains to choose from, it's never been easier to enjoy CBD at home.
What Are the Effects of CBD?
With the background to CBD established, including how it works, and where it comes from, we can finally move onto what the cannabinoid does, and its potential influence.
To be clear: nothing we’re describing below has been proven, and many more studies are needed to confirm the hypotheses presented. We absolutely don’t recommend using cannabis as a substitute for your regular medicine. In fact, if you’re already dealing with health issues, you should ask your doctor before trying any form of cannabis.
Sleep
Sleep is a vital process that gives our mind and body the ability to recover from the day. Unfortunately, sleep is also one of the things many humans tend to neglect, mostly because of our access to entertainment and the stress of our 24/7 society.
Preclinical studies are examining CBD in the domain of sleep. More specifically, researchers are looking to find out how the cannabinoid affects key sleep hormones such as melatonin[1] and cortisol[2].


Relaxation
Unfortunately, tension and uneasiness are never far away in today's modern society. And, to make matters worse, tackling anxiety is not straightforward—how and why it occurs differs from one person to the next.
However, one similarity between all instances of anxiety is the role of 5-HT receptors and the neurochemical serotonin. Nicknamed the happy chemical, serotonin has a direct effect on anxiety through its activation of these receptors and is usually released during physical activities such as exercise or sex.
Encouragingly, researchers have uncovered that CBD also interacts with 5-HT receptors, modulating serotonergic transmission. The Journal of the International Association for the Study of Pain[4] conducted an animal study of neuropathic pain. It concluded that "repeated treatment with low-dose CBD reduces anxiety through 5-HT₁ₐ receptor activation". They went on to add that these results "support the initiation of clinical trials" for CBD-based treatments.

Muscle Recovery
Although inflammation is often portrayed in a negative light, it's a crucial mechanism. It helps our body tackle infections and repair damaged tissue. The latter is especially important not just for athletes, but anyone who wants to stay healthy. Developing stronger muscles reduces the risk of injury, and helps keep us active and on our feet.
However, for us to develop a healthy inflammatory response, we first need a robust immune system. But, for all the good our immune system does, sometimes it gets confused, especially if it's working overtime to repair damaged tissue. It can end up attacking healthy cells rather than toxic ones, which is bad news if you’re trying to promote muscle recovery.
A team of researchers from Mississippi State University in the US is looking to determine if CBD has an impact on the immune response[5], and they are paying particular attention to regulatory cells.


Counteracting THC
When working alongside THC, CBD is believed to negate some of the anxiety that THC causes. CBD appears to also influence the excitatory effects of THC by delaying the onset of the high and how long it lasts.
Specifically, a randomised placebo study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology[6] found that post-THC paranoia was reduced in the group that received an oral dose of CBD. A combination of both CBD and THC could provide a multifaceted approach to well-being while limiting potential side effects.

Epilepsy
Perhaps one of the most encouraging areas of study is that of CBD's impact on epilepsy—specifically Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Both are severe conditions that mainly affect children, and those affected with the worst cases can have hundreds of seizures a day.
In 2018, the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a synthetic version of CBD called Epidiolex. The drug is proving highly effective, significantly improving the quality of life for children living with Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
There are, of course, differences between a purified version of CBD, and the natural version extracted from hemp.

Does CBD Have Any Side Effects?
With so many investigations taking place around CBD, have researchers found any detrimental effects? A comprehensive review[7] by the World Health Organization (WHO), asked the same question, taking an in-depth look at all of the current research on CBD.
After looking through the available data, WHO stated the following:
- CBD is generally well tolerated with a good safety profile.
- Reported adverse effects may be the result of drug-drug interactions.
They also reported some adverse effects from CBD. However, even these appear mild, and they seem to dissipate quickly.
Possible side effects include:
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Upset stomach
- Dizziness
It's important to remember that the majority of these side effects were recorded in studies where the administered dose was significantly higher than everyday scenarios. That being said, CBD does affect everyone slightly differently, so it's important to start with a low dose until you become accustomed to its effects.
Another substantial side effect highlighted by the WHO was the possible interaction between CBD and existing medications. Evidence suggests CBD can interfere with the breakdown of specific medicines, and you must consult with a doctor or physician if that applies to you. The interaction may not cause any problems, but your doctor will be able to give you case-specific advice.
Is CBD Psychotropic?
Despite its links to the Cannabis sativa species, CBD is not psychotropic, although it may be considered psychoactive. The confusion on this issue usually stems from its association with THC. Although CBD and THC are both cannabinoids, the way they interact with the body differs significantly, and so does their effects.
THC produces a high because of its affinity for CB1 receptors in parts of the brain linked to mood and motivation. This unique interaction is why cannabis remains prohibited in much of the modern world. CBD, on the other hand, doesn't show an affinity for the same CB1 receptors. Instead, it works behind the scene to support the entire ECS, and does not produce psychotropic side effects as a result.
Can You Develop a Tolerance to CBD?
Another common question is whether repeated use of CBD leads to tolerance, and a need to consume increasing amounts to feel the same effects.
Again, to answer this, we have to refer to the experts on the matter— WHO. As part of their 2018 review, they also identified that "CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential", going on to add "there is no evidence of recreational use of CBD or any public health-related problems". There's still a lack of long term studies (CBD research is fairly new), but the evidence is encouraging.
Methods of Consuming CBD
The potential of CBD appears vast, but not nearly as comprehensive as the products available. CBD's lack of toxicity has led to a broad range of options, each with unique advantages and disadvantages.

CBD Oils
CBD oils placed on or under the tongue remain the most popular way to enjoy the compound. Thanks to the olive, hemp and MCT oils that carry it, the absorption rates are quite high. CBD is naturally hydrophobic (repels water), so the body has a tough time absorbing it without the help of a carrier oil.
Swallowing it won’t work too well, and you’ll need more to obtain the desired effects. If you take it sublingually (under the tongue), though, it’ll get absorbed into the mucus membrane and hit your system directly.
Smoking CBD
Smoking CBD benefits from a much higher bioavailability compared to other consumption methods. Bioavailability is an important concept because it's an indication of how much and how fast CBD reaches its target area—the bloodstream.
In this case, active CBD reaches the bloodstream incredibly quickly, thanks to capillaries in our lungs. As such, you'll feel effects in as little as 15 minutes, but the trade-off is they won't last as long compared to CBD edibles or oils.
CBD-rich cannabis strains, of course, also contain a variety of other cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. You'll not only get the potential entourage effect benefits, but experience a diverse range of flavors and tastes as well.

Vaping CBD
Provided you invest in a decent vaporizer, vaping has some significant benefits over smoking. First, vaporizers don't burn what you’re smoking, so you reduce the risk of harmful substances entering your lungs.
Second, the bioavailability of vaping is just as good as smoking (if not higher), and people tend to ask fewer questions if you pull out a vaporizer, compared to a joint.

CBD Edibles
Cannabis edibles may have started as cookies and brownies, but now that’s just the tip of the iceberg. This interest in edibles is not without good reason, either. Cannabinoids like CBD have a natural taste, and although it isn't bad, per se, it's not for everyone.
Consuming CBD edibles also changes the way we feel its effects. Onset is delayed (takes up to an hour), but effects last much longer. This makes them ideal when you can't quickly top up on CBD and need longer relief.

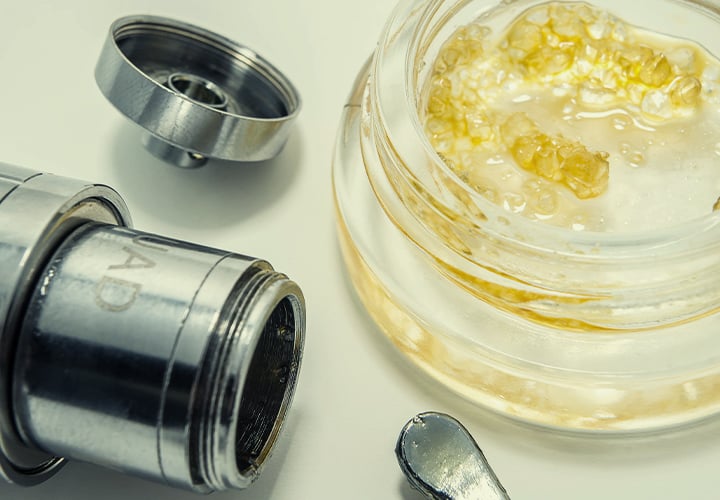
Dabbing CBD
You'll need a dab rig and a few other tools to match, but dabbing is the ultimate experience for seasoned CBD users. We say ultimate because it provides a highly concentrated dose that isn't recommended for newcomers.
By flash vaporizing CBD concentrate (CBD isolate, CBD wax, and CBD shatter), you'll experience incredibly pronounced effects in seconds. Carrying a dab rig around isn't at all convenient, but for some, the potency will be a worthy compromise.


CBD Tinctures and Sprays
CBD tinctures are very similar to CBD oils, but you take them sublingually.
Supplements taken under the tongue don't have to contend with our digestive system. Instead, they enter the bloodstream directly thanks to tiny capillaries in the mouth. If you need quick relief, CBD tinctures take effect in as little as 15 minutes.
The same goes for CBD sprays. The inside of your nose contains hundreds of small blood vessels, so CBD has a direct route to your bloodstream.
It's also possible to find CBD tinctures in a range of flavors, making them a little more appealing than oils. That being said, you lose out on the secondary benefits offered by carrier oils, so the decision comes down to personal circumstances and what is best for you.

CBD Topicals, Transdermal Patches, and Suppositories
CBD topicals are straightforward to use (simply rub into the skin) and suitable for all manner of skin types. Rather than entering the bloodstream, active ingredients focus solely on receptors at a local level, helping to soothe, moisturise and protect the skin.
Transdermal patches take things one step further. By blending CBD with certain drugs, it's possible for the cannabinoid to permeate the skin and enter the bloodstream. These patches work in the same way as a nicotine patch, providing a slow release of active ingredients.
If you want to take active absorption a step beyond transdermal patches, then consider CBD suppositories. They offer a (potentially) higher uptake of CBD, while also being incredibly discrete. Be warned though, the bioavailability of CBD suppositories remains under review, and it's not known exactly how effective they are.

Different Carrier Oils for CBD
As mentioned, CBD extracts must be infused in a carrier oil (or some other base) in order to be stored and then used. There are many different oils available, each with their own benefits and drawbacks. Ingesting CBD as an oil increases its bioavailability as it passes through the body via the lymphatic system, rather than going directly into the bloodstream.
1. Olive Oil
Healthy and delicious, olive oil is a popular carrier oil for CBD extractions. It is rich in oleic acids, fatty acids, and antioxidants, which means you’re getting more than just the benefits of CBD.
2. Hemp Seed Oil
Hemp seed oil is likewise very rich in omega-3 and 6, as well as a range of other potentially beneficial compounds. Moreover, why not suspend your CBD extract in oil made from the cannabis plant’s seeds?
3. MCT Oil
CBD MCT oil is derived from coconut oil, and is considered to be the best CBD carrier oil. This is because it is easily digested and is therefore believed to increase the bioavailability of CBD, making the product more efficient.
4. Black Seed Cumin Oil
Black seed oil has long been used for holistic purposes in parts of the Middle East. Made from nigella seeds, this oil is very rich in antioxidants and is believed to have a wide range of potential wellness benefits.
What Does CBD Oil Taste Like?
People often wonder if CBD oil has any flavor. Well, it does, and it tends to depend on the type of carrier oil used. Full-spectrum and broad-spectrum CBD products have a distinctly “hempy” flavor, as they contain many of the compounds found in hemp plants. With isolates, the CBD has no flavor, and whether the oil tastes of anything will depend on the carrier oil used. In general, though, oils tend to have an earthy flavor.
How to Make CBD Oil Taste Better
Consider the following methods to improve the flavor of your CBD oil experience:
- Wash it down with a tasty drink: this may seem obvious, but it can work! After letting the oil sit under your tongue for a minute, wash it down with a drink of your choice.
- Chew a mint before or after to cover the taste. Also, if you make your own CBD oil at home, you could even add mint to it so the oil has a minty flavor.
- Add the oil to food/drink, and swallow it. This way, you don’t have to taste it at all.
- Buy an odourless and flavorless CBD product.
- Eat CBD gummies, which taste sweet, not hempy.
How to Dose CBD
Every CBD manufacturer provides a recommended dose, but they’re just that— recommendations. It's essential to know that there is no ideal dose of CBD, and how much you should take is based on factors including:
- Metabolism
- Body fat
- Product strength
- Health issues
There are, however, some general guidelines you can follow until you find the dose that's right for you.
- Start with a low-concentration CBD oil: Stick to a low-concentration oil for at least two weeks. It'll give you time to get accustomed to the effects and deal with any potential side effects.
- Take CBD once or twice a day: Although most recommendations state "up to three times a day", try it once or twice at first. Again, this gives you time to find what works for you.
- Stick to the same routine for at least two weeks: CBD takes effect very quickly, but give yourself at least two weeks to get acquainted with your routine.
- Wait to combine CBD products: It's entirely possible to combine different CBD products, but again, stick to the same routine so you can adjust the effects accordingly. There's nothing wrong with eating some CBD edibles in the morning, then vaping CBD flower in the afternoon.
- Speak to your doctor: We can only speak generally, but your primary care doctor can give case-specific advice. If you're using CBD to address a particular condition, they may have valuable insight on a recommended dose.
 CBD Dosage Calculator
CBD Dosage Calculator
 CBD Dosage Calculator
CBD Dosage Calculator
Microdosing CBD
Microdosing is a viable strategy that works well with CBD because it counteracts one of the compound’s main disadvantages. See, the cannabinoid has a very short half-life (the length of time it remains in the body), so regular consumption is a must if you want to make the most of its influence.
The key to microdosing is taking small, frequent doses. However, just like regular dosing, you'll need to experiment with different routines to find what works for you. If it's convenient to do so, try splitting your daily intake of CBD into smaller portions throughout the day.
CBD For Pets
With the basics of CBD in humans covered, it makes sense to turn attention towards our feline and canine companions. Why? Because just like us, both cats and dogs have an endocannabinoid system.
Most of the data regarding CBD's effect on pets remains anecdotal, but there are a handful of in-vivo studies to go on. Possible effects appear similar to those in humans, with CBD influencing their brains, along with their nervous, immune and digestive systems. These investigations are looking to see if CBD impacts the nervous, immune, and digestive systems.
Be careful, though; not all CBD products are suitable for pets. Both cats and dogs are much more sensitive to the smaller compounds found in hemp (terpenes and flavonoids). As such, pet-focused CBD products have these elements removed to make them pet-safe, while regular CBD oils do not.
Is CBD Legal?
The legality of CBD remains a contentious issue. In most of the modern world, CBD is legal to buy and use, but there are restrictions. CBD products must be derived from hemp and contain no more than 0.2% THC (Europe). The legal limit of THC is slightly higher in the U.S. (0.3%), but you get the idea—restrictions vary depending on where you live, and it's a difficult situation to navigate.
You must check with the local authority in your home nation before trying CBD. In most cases, it'll be fine, but it doesn't hurt to double-check. You should also source CBD from a trusted supplier, avoiding any that don't independently test their products. Without confirmation of what, exactly, is in every batch of CBD, you won't know if there's an issue until it's too late.
- Cannabinoids attenuate norepinephrine-induced melatonin biosynthesis in the rat pineal gland by reducing arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase activity without involvement of cannabinoid receptors https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com
- Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The effects of cannabinoid administration on sleep: a systematic review of human studies https://www.med.upenn.edu
- Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Immune Responses Regulated by Cannabidiol https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- SAGE Journals: Your gateway to world-class journal research https://journals.sagepub.com
- https://www.who.int/medicines/access/controlled-substances/CannabidiolCriticalReview.pdf