.
CBD and Cardiovascular Disease: What You Need To Know
The leading cause of death globally, cardiovascular disease (CVD) is an umbrella term that includes numerous dramatic conditions. Keep reading to find out what you need to know about CVD, including the potential role of cannabidiol (CBD) in facing this group of illnesses.
Contents:
The cardiovascular system plays a vital role in the body. Comprising the heart, blood vessels, and the blood, this system is responsible for the critical task of transporting nutrients, hormones, and oxygen to cells via the bloodstream. In combination with the lungs and kidneys, it also disposes of waste products via lung exhalation or urine formation; removing from the body products such as carbon dioxide or nitrogenous compounds.
Given the importance of the cardiovascular system, it will come as no surprise that any malfunctioning or disorder could have catastrophic consequences. Unfortunately, that's the reality facing millions of people worldwide.
Follow along as we explore the details surrounding cardiovascular disease, and see if CBD presents any avenues for addressing this global health issue.
What Is Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)?
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. Conditions within this category include:
| Heart valve diseases | Hypertension | Coronary heart disease | Heart arrhythmia |
Diseases of the arteries (Atheromatosis) |
| Heart valve diseases | Hypertension | ||||||
| Coronary heart disease | Heart arrhythmia | ||||||
| Diseases of the arteries (Atheromatosis) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
There are numerous causes of cardiovascular diseases, but lifestyle is a major factor. This is somewhat of a blessing and a curse. On the one hand, changes to diet, exercise, and the reduction of tobacco use can significantly improve quality of life. However, the caveat is that of the 17.9 million people affected by CVD in 2019[1], many cases were preventable.
-
Are Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Disease the Same?
It's a common question, but one worth clarifying. When we talk about cardiovascular disease, we refer to several conditions affecting the heart (cardio) and the blood vessels (vascular). Heart disease focuses specifically on heart conditions such as coronary heart disease, heart arrhythmia, and valve heart diseases.
Of course, given how closely linked these systems are, it's common to see overlap, with conditions that technically fall under both categories. The simplest explanation is that all heart diseases fall under the umbrella of cardiovascular disease, while not all cardiovascular diseases affect the heart.
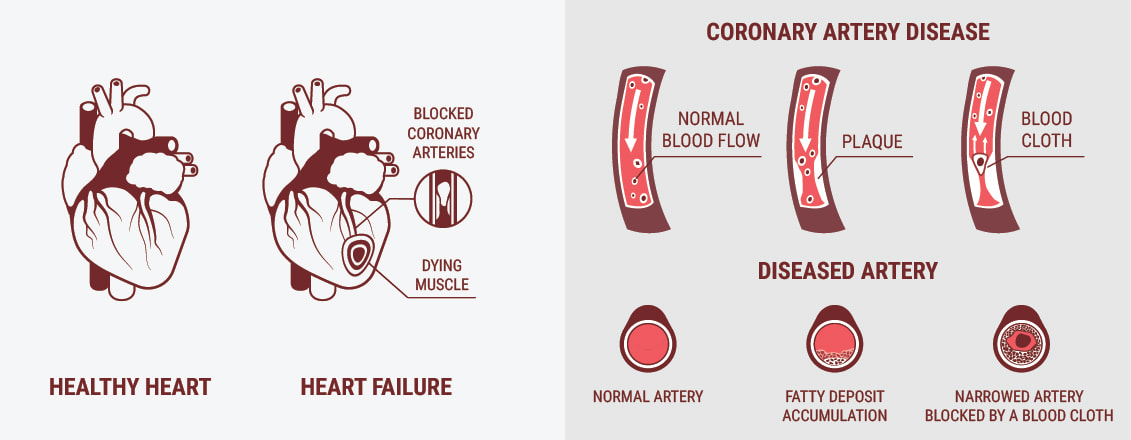
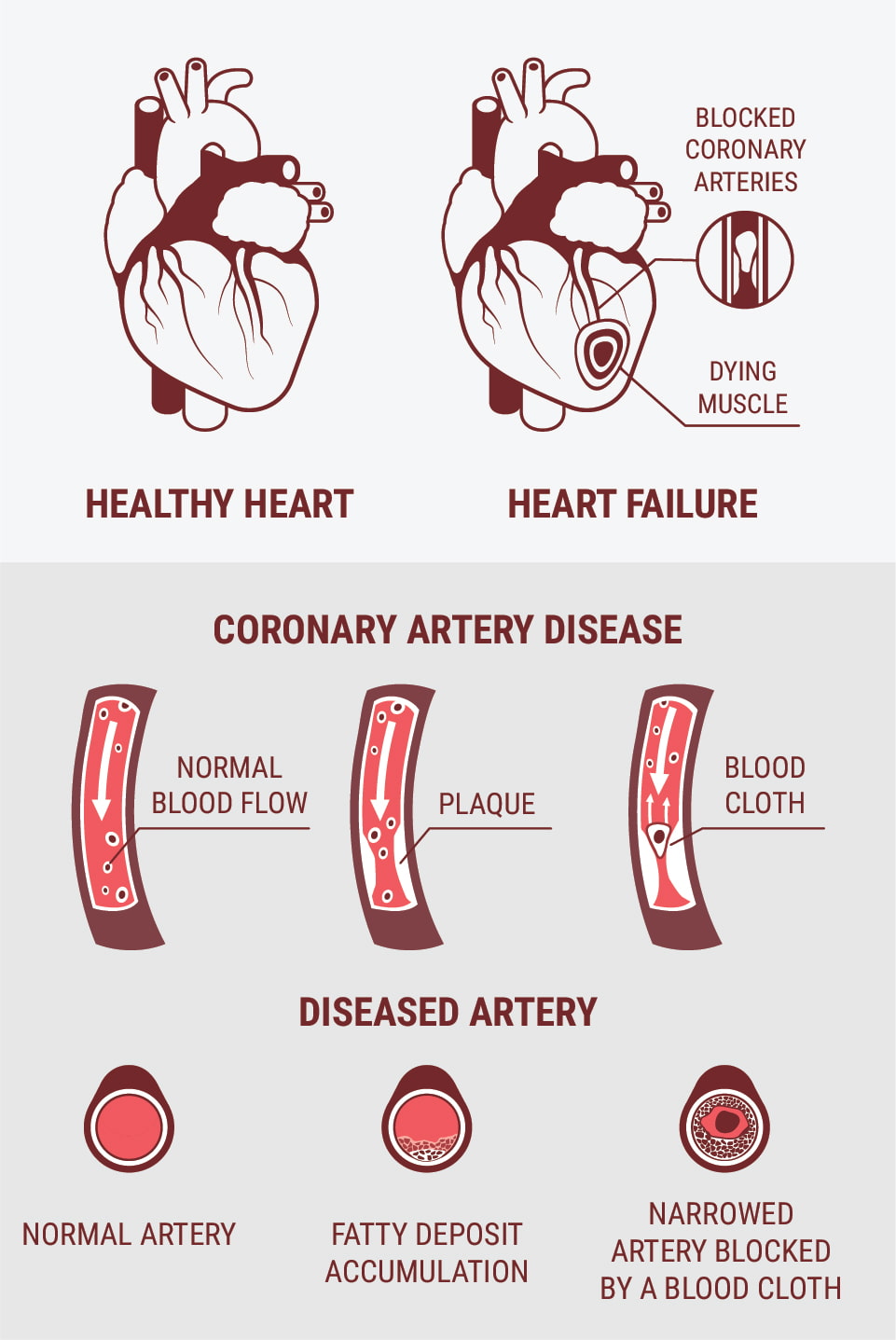
Types of Cardiovascular Disease
We briefly mentioned several of the conditions under the cardiovascular disease umbrella, but given the prevalence and severity of CVD, it's worth taking a closer look at some of them. Understanding cardiovascular diseases and their origins, or etiology, will also help us better understand the role of the endocannabinoid system, and why researchers are looking at the impact of compounds like CBD.
Some cardiovascular disorders include:
| Deep vein thrombosis | Usually affecting veins in the lower leg, thigh, and pelvis, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that can be very dangerous if left untreated. Symptoms typically manifest as swelling, throbbing, and red or darkened skin (in the affected area). |
| Rheumatic fever | Rheumatic fever develops due to complications of bacterial throat infections. Symptoms include fever, heart failure, and swelling of the joints. |
| Coronary heart disease | Mostly the result of lifestyle choices, coronary heart disease (CAD) occurs when fatty deposits block or limit blood flow in the heart's main arteries. Symptoms start as chest pains (angina), often associated with shortness of breath, but can quickly worsen. |
| Peripheral arterial disease | With a similar obstruction mechanism to CAD, peripheral arterial disease occurs because of blocked arteries, this can affect legs, arms or kidneys, rather than the heart. Symptoms vary depending on the organ affected. |
| Stroke | Left unchecked, peripheral arterial diseases will ultimately lead to a stroke. This occurs from a lack of blood supply to your brain, often by arterial carotid obstruction. Strokes are also caused by burst blood vessels. These are known as hemorrhagic strokes. |
| Deep vein thrombosis | Affecting veins in the lower leg, thigh, and pelvis, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that can be very dangerous if left untreated. Symptoms typically manifest as swelling, throbbing, and red or darkened skin (in the affected area). |
| Rheumatic fever | Rheumatic fever develops due to complications of bacterial throat infections. Symptoms include fever, heart failure, and swelling of the joints. |
| Coronary heart disease |
Mostly the result of lifestyle choices, coronary heart disease (CAD) occurs when fatty deposits block or limit blood flow in the heart's main arteries. Symptoms start as chest pains (angina), often associated with shortness of breath, but can quickly worsen. |
| Peripheral arterial disease | With a similar obstruction mechanism to CAD, peripheral arterial disease occurs because of blocked arteries, this can affect legs, arms or kidneys, rather than the heart. Symptoms vary depending on the organ affected. |
| Heart attack and stroke | Left unchecked, peripheral arterial diseases will ultimately lead to a stroke. This occurs from a lack of blood supply to your brain, often by arterial carotid obstruction. Strokes are also caused by burst blood vessels. These are known as hemorrhagic strokes. |
Traditional Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
It depends on the severity of the condition, but much of the focus for CVD treatment is lifestyle adjustments. Not only are these a great way to prevent disease in the first place, but they can help to rehabilitate patients.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, changes to diet, and a balanced approach to alcohol can significantly change CVD severity. In fact, it's thought that most cases of cardiovascular disease could be avoided by addressing what the World Health Organization calls "behavioural risk factors".
- Medical intervention: For more severe instances of CVD, doctors usually prescribe medication or even surgery. Both focus on improving blood flow, via repairing damaged arteries, restoring a regular heartbeat, or replacing heart valves.
Understanding the Role of the ECS in Cardiovascular Disease
It's now time to dive into the role of the endocannabinoid system in heart health[2]. Research is ongoing, but from what is understood so far, the ECS plays a supportive role in heart health, stepping in when it detects a stressed or unbalanced state. The ECS in the heart contains a combination of CB receptors, non-CB receptors, and endocannabinoids (internally produced compounds similar to the cannabinoids found in cannabis).
-
Cannabinoid Receptors
Starting with cannabinoid receptors, there are two main types, CB1 and CB2. Both exist all over the body, but for the heart, we're primarily interested in CB2 receptors (the one linked mainly with CBD). Animal studies[3] suggest that activation of CB2 receptors may influence cases of atherosclerosis and ischemia.
-
Endocannabinoids
Then, there's the proposed role of endocannabinoids, most notably anandamide (AEA). Things get a little more complex here, as scientists still aren't sure which receptor(s) anandamide acts upon. What they have found, however, is that anandamide may play a part in the relaxation of arteries and other aspects of cardiovascular disease, according to a 2001 murine study from the University of Cambridge[4].
If anandamide could prove helpful to heart health, there's a catch—the endocannabinoid doesn't hang around for long. This is a result of a naturally occurring enzyme called FAAH, which decompounds AEA into two smaller metabolites.
CBD and Cardiovascular Health
Studies investigating the interaction between anandamide and FAAH have led researchers to CBD. It appears that cannabidiol may inhibit moderately the FAAH[5] activity, subsequently raising levels of anandamide inside the body.. Given the current understanding of anandamide in heart health, this could prove a useful interaction. Still, as we pointed out, there are several “potential” mechanisms of action, and much more research is needed to verify any findings.
Then, there's the balancing influence of CBD on the endocannabinoid system as a whole. Cannabidiol differs from compounds like THC or CBN which mainly bind to the CB1 receptors, and instead have a much greater affinity with CB2 receptors.
With that in mind, it’s easy to see why scientists are keen to explore the influence of CBD [6]. For the proper treatment of cardiovascular diseases, a correct understanding of the endocannabinoid system is essential if CBD is to be beneficial.
-
What Are the Risks of CBD?
Some research into the impact of CBD on conditions such as hypertension[7] and ischemia induced cardiac arrhythmia[8] has taken place.. But here is where we encourage caution on the topic. One relevant study used a tiny sample size, while another was examining an animal model.
Because it's too early to talk about practical application, it's also premature to say that there aren't any risks. The honest answer is that we just don't know either way. We've previously explored the prospect of cannabis, CBD, and THC on hypertension, but it's important to remember that decreasing heart rate is a double-edged sword. Lower heart rate in healthy individuals is generally a good thing, but if your heart rate is too low, the potential for syncope or ischemia by a blood flux becomes greater, and especially dangerous in patients with artery obstructions.
The final watch-out with CBD is its potential interaction with certain medications. Earlier, we highlighted how prescription medication is often used to treat cases of CVD. For alternative treatments to be effective, they would need to work alongside existing therapies, and there are still a lot of variables to explore in this regard.
Is the Cardiovascular System a Target for CBD?
There's a lot to unpack with CBD and the cardiovascular system, so it's worth recapping the ground we've covered. Cardiovascular disease is a prevalent problem affecting millions of people worldwide—the need for effective treatments is a top priority. The difficulty, of course, is that the cardiovascular system runs throughout the body, which makes finding drugs and treatments for it very challenging.
Underpinning the cardiovascular system is the endocannabinoid system, a regulatory network that helps to balance the body's needs. Researchers believe that the ECS could play a crucial role in heart health, so exploring its full potential is vital. This brings us nicely to CBD, a compound found in cannabis and hemp that may improve the functionality of the ECS. There's still plenty of dots to connect, but the good news is, researchers remain hopeful on the relationship between CBD and cardiovascular disease.
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) https://www.who.int
- Endocannabinoids and the Heart https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The Endocannabinoid System and Heart Disease: The Role of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Mechanisms of anandamide-induced vasorelaxation in rat isolated coronary arteries https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia | Translational Psychiatry https://www.nature.com
- Is the cardiovascular system a therapeutic target for cannabidiol? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- A single dose of cannabidiol reduces blood pressure in healthy volunteers in a randomized crossover study https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Acute administration of cannabidiol in vivo suppresses ischaemia-induced cardiac arrhythmias and reduces infarct size when given at reperfusion https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov