.

The Most Common Cannabis Mutations
Ever seen ducksfoot cannabis? What about a variegated plant? While not common, the cannabis plant has quite a few interesting mutations that sometimes can even boost yield. Here is a list of the most common or intriguing mutations of the cannabis plant.
Everyone knows what a cannabis plant looks like, right? Actually, not so fast! Not all cannabis looks the same. With the rise of hybrid experimentation, mutations are increasingly common, if not deliberately bred into strains downstream. Certain strange mutations have actually become the basis for some of the most popular strains out there.
But what do these mutations look like? And what do they mean for the plant? If not your yield?
Contents:
Twin Seedlings
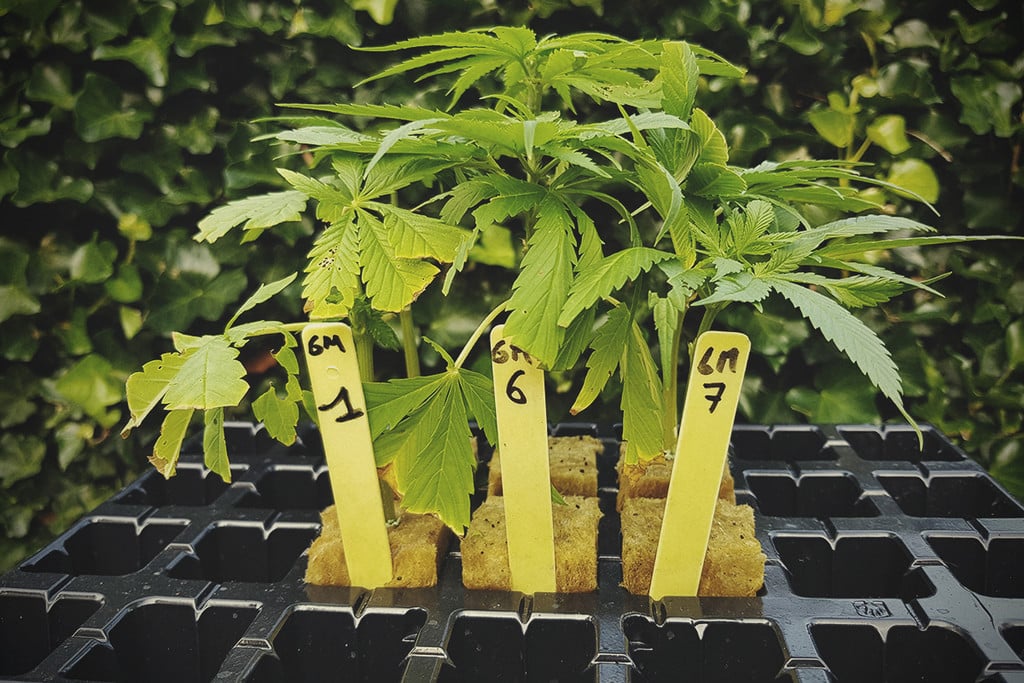
After placing a cannabis seed in the soil, growers expect one shoot to emerge several days later—not two! However, just like human twins develop in the same womb, two seedlings occasionally emerge from the same seed. Botanists refer to this phenomenon as polyembryony. It occurs either when more than one embryo develops in a single seed or as a result of the cleavage of a fertilised ovum.
Twin Cannabis Seedlings: Good or Bad?
You’re the parent of plant twins. Should you celebrate? Or is it a cause for concern? It totally depends on the grower. If you’re looking to remain stealthy with a micro grow, then you’ll want to snip one of the seedlings just above the soil surface and discard it. If you have the desire to grow more plants, then you can pry these two babies apart and grow them into highly uniform plants.
How to Separate Twin Cannabis Seedlings
If you want to keep your twins, you'll need to separate them to prevent stunted growth. Follow these steps to do so without causing any damage to your young plants.
Step 1: Extract Seedlings
Start by removing your twin seedlings from their growing medium. If you sowed directly into soil, dig under the roots and pry them out. If you sowed into a soil plug or rockwool cube, carefully tear the growing medium apart and extract the seedlings.
If you germinated seeds in a cup of water or between moist paper towels, you’ll have immediate access to the root system and won’t have to mess around with any growing medium.
Step 2: Clean and Untangle
Next, gently dip the root system of your seedlings into a glass of water to remove most of the debris surrounding the roots. Now, slowly and carefully untangle the roots, and gradually pull them apart until separated.
Step 3: Inoculate
If you have any to hand, dip the roots into arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi spores. Alternatively, add propagules into their new growing medium. These microbial allies will help your seedlings grow into large, healthy plants and minimise the threat of fungal infections and damping off.
Step 4: Transplant
Once separated and inoculated, transplant your seedlings into their new homes, and give them a light watering to help keep them turgid.
Foxtailed Cannabis
This mutation is caused by calyces that grow stacked on top of each other. This creates a very oddly-shaped bud formation. This is not a detrimental mutation, but it is not necessarily beneficial either. This mutation breaks up the bud structure of the plant. Instead of growing into a rounded shape, the bud spreads out in an elongated way. It can also show that your plants are not ripening in the right way.
Heat and light stress can also cause this mutation. The calyxes literally form spires.
Foxtailing is not always an anomaly. Some Purple or Cole Train strains commonly produce foxtailed bud structures. Strains that hail from Colombia or Thailand also commonly exhibit these characteristics.


Ducksfoot Cannabis
This mutation hails from Australia. A breeder then took advantage of the odd variety by cultivating it into a real “strain” - although the leaf mutation can occur across various strains. This mutation gets its name from the webbed, foot-like leaves that it grows. However, the different looking leaves are just the start of it. Most ducksfoot cannabis grows up to be sativa plants.
This strain is great for camouflage. Ducksfoot cannabis looks very unlike “normal” cannabis. Thus, it is perfect for cultivators in jurisdictions where growing is still verboten. The plant will also produce beautiful purple buds if the temperature is cold enough.
Variegation
Variegation is one of the most beautiful cannabis mutations. This can occur either fully or partially in different sections of the plant where white (or yellow) and green parts coexist. This mutation results from a plant’s inability to produce chlorophyll. It can occur on leaves, the heads of buds, or can wash out the entire plant in white.
In the most extreme cases, plants will not live very long as chlorophyll is necessary in the production of sugars for plant energy and development.
Variegation also means lower yields. A lessened ability to photosynthesise equates to slower growing plants. That said, some variegated plants can grow to be quite tall.


Whorled Phyllotaxy
This kind of mutation is also very pretty. Cannabis plants have a great deal of natural geometry. This mutation creates a slightly different kind. Regular plants have two leaves that grow from each internode. Whorled phyllotaxy plants have three leaves instead. Plants with a whorled phyllotaxy tend to be extra bushy. That said, the trait is not useful to breeders as it can lead to greater yields, but will disappear once attempted to be bred and replicated.
Creeper Cannabis
Creeper cannabis tends to exhibit itself in tropical strains. These strains are already large and grow in humid conditions. The plant’s lower branches bow down to touch the ground. Once they reach the floor, the branches continue to grow, even forming new root sites. This phenotype is super useful for disguising grows. However, creeper cannabis is a rare mutation and has not been developed commercially.


Australian Bastard Cannabis
ABC is an Aussie invention. It was first “discovered” near Sydney in the 70’s. This strange anomaly grows more like an herb than a shrub. The leaves are not serrated; instead they’re smooth and shiny, growing no more than 5cm in length.
The original ABC was more like hemp and was low in all cannabinoids. However, underground breeders managed to boost the THC levels. This mutation made ripples about a decade ago. No strains have (yet) been made commercially available.
Vine Cannabis
Is it a true breed or just an extension of ABC? Nobody really knows. But Aussie breeders claim that ABC crosses can produce vine-like mutations in the plant. This includes the ability to form stems that wrap in a pattern around each other.
The mutation is extremely rare. It may only exist because of deliberate breeding to trigger this effect. While this trait is interesting, it is not advantageous to yield or cannabinoid concentration. No commercial strains currently incorporate this mutation.
Leaf Buds
Most flower sites on cannabis plants occur at the nodes, where the stalks originate. However, leaf buds occur at the base of the leaves themselves. This is an unusual (if pretty) mutation. It can also be advantageous to yield because the plant grows more bud sites. However, experienced growers tend to remove them as they form; they take up nutrients that can otherwise nourish the main flower sites.


Polyploidism
Polyploids in nature are organisms that possess double the number of chromosomes than their non-mutant genetic twins. This trait can sometimes be fixed into plant species via selective breeding. Cannabis plants can spontaneously develop polyploidism. It can also be induced in plants via treatment with a powerful chemical called colchicine.
This is a hugely useful trait for significantly increasing THC production, as well as yield. Extra-large plants produce extra-large buds, of course. At this time, there are no true-breeding strains with this mutation that have been stabilised.
Upright Phenotype
This is a common mutation, particularly in hybrid strains. The plant develops into a truly massive form - much like a tree. These massive cannabis plants look like indicas, but have the height of tropical sativas. This phenotype has one massive stalk that can grow up to 4m high. The plant looks either like a Christmas tree or a candelabra. The leaves are narrow, unlike the wider leaves of landrace sativas. While the plant is absolutely impressive and yields are prodigious, its height is a disadvantage in indoor grows.








































