.

CBD and Hormonal Balance
Studies show that the endocannabinoid system activates receptors in the endocrine system, and ongoing research aims to explore if CBD impacts this system in a way that influences sleep, stress, sexual function, and energy consumption. New cannabinoid therapies for endocrine disorders such as diabetes and menopause bone diseases are expected.
CANNABINOIDS TALK TO THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Just like endocannabinoids, hormones are biochemical messengers involved in many aspects of our physiology. Our growth, behaviour, sleep, sexual function, energy consumption, and mood are all affected by hormones. Even our capacity to evaluate danger and elaborate a proper response depends on these compounds.
These natural regulators are produced by the endocrine system in glands such as the thyroid, pancreas, pineal gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, ovaries, and testicles. The hormones released by these glands include melatonin, testosterone, insulin, cortisol, glucagon, epinephrine, and many others. As an example, cortisol is the hormone that manages our response to stress and anxiety, while melatonin indicates to our body when it’s time to go to sleep and when to wake up. Internal or external factors such as ageing, stress, nutrition, and chemicals can unbalance the production of these messengers.
Our endocannabinoid system is closely linked to the endocrine system. Studies have shown that the endocannabinoid system activates receptors in the endocrine system, and that cannabinoid receptors have been found in many different endocrine glands. Consequently, CBD too can activate endocrine receptors in the brain, as much as all over the body.
Studies have shown that this cannabinoid actually interacts with the endocrine system, affecting processes like sleep cycle, stress signals, metabolism, and sexual activity. Some studies even indicate that endocannabinoids can control the proliferation of numerous types of endocrine cancer cells, leading to antitumor effects[1]. In particular, they are able to inhibit cell growth and metastasis in some kinds of oncologic diseases, such as thyroid, breast, and prostate tumours.
The relationship between cannabinoids and hormone production suggests that these natural compounds may have therapeutic potential for treating endocrine disorders. One of the many challenges for cannabis science today is to understand how the endocrine system can be modulated by CBD and other cannabinoids in order to regulate hormone levels.
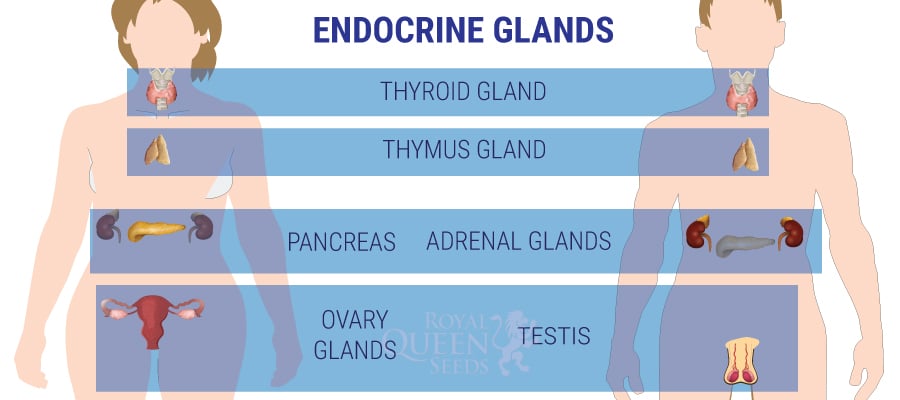
CBD AND METABOLIC HORMONES
Diabetes is one of the most common endocrine diseases, caused by reduced insulin production in the pancreas. Insulin balances our metabolism and energy levels by regulating nutrient absorption and storage, and by turning sugars into energy. Insulin imbalances can cause obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
A wide variety of studies have explored the effects of cannabinoids on metabolism, as well as the relationship between CBD and diabetes. Research teams are now looking to see if CBD can impact pancreas function, blood sugar level, and energy balance[2]. Following conclusive findings, insulin modification could be one of the next big things in cannabis application.
CBD AND SEXUAL HORMONES
In both males and females, the secretion of sex hormones is directly controlled by the pituitary gland and influenced by the hypothalamus. It appears that here too cannabinoids exert an action on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. There is an evident connection between endocannabinoid activity and the production of the female hormone estradiol. The endocannabinoid system has been found to contribute to the regulation of the menstrual cycle. The mechanisms are not well understood, but it appears clear that the endocannabinoid system impacts the release of gonadal hormones. Unfortunately, THC altered hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal integrity and affected reproductive function in female mice. Chronic CBD exposure promoted impairment in sexual behaviour[3] and fertility of male mice as well.
One area of cannabis science that’s showing great promise is the treatment of bone and joint diseases with cannabinoids. During menopause, fluctuations and a general reduction in sex hormones result in weaker bones and characteristic loss of bone density in women. Excessive GPR55 receptor activity is involved in this process, leading to bone tissue loss and, eventually, osteoporosis.
Some academics have labelled GPR55 as the third cannabinoid receptor (CB3), and CBD manages to temporarily block it. Researchers are now testing this mechanism[4] in models of bone remodelling and bone density loss.
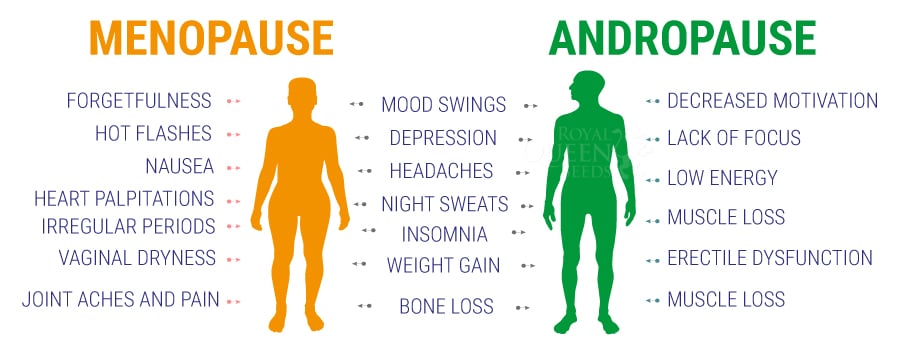
CBD and Sleep Hormones
Drugs that influence sleep hormones in a positive way can “hack” the endocrine system to help people achieve a good night's sleep. Does CBD belong to this pharmacological pantheon? Researchers are trying to find out. High levels of the hormone cortisol, caused by stress and poor nutrition, are thought to negatively impact sleep.
Human trials are now looking to see if CBD holds any sway over cortisol levels[5]. The hormone melatonin also plays a key role in initiating sleep; studies are attempting to find out what CBD application does to reduce[6] or boost this crucial chemical.
CBD, Sleep, and a Holistic Approach
The research on CBD and sleep remains early and inconclusive. As scientists continue their investigations, doctors recommend several lifestyle modifications to promote restful sleep. These changes include following a strict sleeping schedule, exercising more often, consuming a balanced diet, and reducing worrying through practices such as meditation.
- Endocannabinoids in endocrine and related tumours. - PubMed - NCBI https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The emerging role of the endocannabinoid system in endocrine regulation and energy balance. - PubMed - NCBI https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Chronic cannabidiol exposure promotes functional impairment in sexual behavior and fertility of male mice. - PubMed - NCBI https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The putative cannabinoid receptor GPR55 affects osteoclast function in vitro and bone mass in vivo https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabinoids attenuate norepinephrine-induced melatonin biosynthesis in the rat pineal gland by reducing arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase activity without involvement of cannabinoid receptors https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com