.

What Is Epidiolex and What Does It Do?
As an oral cannabis-based medicine designed to combat seizures, Epidiolex contains high concentrations of CBD. The FDA approved the use of the drug following a series of trials revealing its efficacy. Now, additional studies are exploring its use for conditions such as chronic pain and anxiety. But how does it compare to CBD oil?
Contents:
Epidiolex belongs to a group of products known as cannabis-based medicines. Whereas whole-plant extracts contain hundreds of different phytochemicals, cannabis-based medicines harness 1–2 molecules of interest. In the case of Epidiolex, manufacturers set their sights on the non-intoxicating cannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol).
Following a set of human trials, Epidiolex won Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in the United States for the treatment of severe forms of epilepsy. Find out everything you need to know about this formula, how it works, and how it compares to CBD oil.
What Is Epidiolex?
Epidiolex made history as the first FDA-approved prescription CBD product. The innovation stems from the UK-based company GW Pharmaceuticals, which also created Sativex—a balanced concoction of THC and CBD. Each bottle of Epidiolex contains 100ml of oral solution and a total CBD content of 10,000mg.
The FDA gave the green light for Epidiolex specifically to treat patients experiencing seizures associated with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome. Because these neurological conditions also affect young children, the administration has indicated the use of the preparation for patients as young as two years old.[1] So far, over 15,000 people have received Epidiolex to combat these conditions.[2]
When Was Epidiolex Approved?
The FDA approved Epidiolex on June 25th, 2018. After decades of federal prohibition, this move signalled a huge shift in the perception of cannabis within the upper echelons of authority. Many cannabis purists argued, and still argue, that this move only served to benefit mega-corporations in their efforts to patent and profit from the plant.
Whether true or not, from the perspective of parents looking to reduce seizures in their children, federal approval of Epidiolex opened legal avenues to potential relief.
This decision followed a series of controlled clinical trials that showed significant seizure reduction in participants treated with the cannabis-based medicine. As more trials are conducted, other cannabinoid formulations may become approved and available in the future.
FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD stated during an FDA news release: “This approval serves as a reminder that advancing sound development programs that properly evaluate active ingredients contained in marijuana can lead to important medical therapies. And, the FDA is committed to this kind of careful scientific research and drug development”.[3]


How Epidiolex Works
Epidiolex harnesses the power of CBD to target a variety of receptors involved in epilepsy. Many cannabinoids, including THC, exert their action through the endocannabinoid system (ECS)—a “universal regulator” of the human body. CBD, however, has a low binding affinity to the major receptors that make up this system. Instead, ongoing studies suggest it helps to balance out neurotransmitter firing through a number of other sites.
The Science Behind Seizures
Before we delve into how Epidiolex works at the cellular level to combat seizures, we need to make sense of how seizures arise in the first place. Under normal conditions, neurons in the brain exist in a state of balance. The electrochemical signals that flow through them are tightly controlled by the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate and the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA.
While at rest, neurons contain a bunch of positively charged potassium ions—the mineral we ingest every time we chew into a banana. However, a much greater number of positively charged sodium ions sit on the other side of the cell membrane, causing the inside of the neuron to maintain a negatively charged state.
Once an electric pulse (known to science as an action potential[4]) hits a particular neuron, it causes channels dotted along the membrane to open. Sodium rushes into the cell while potassium rushes out. This causes the neurons to flip from being negatively charged to positively charged, and carry the signal down its neck (the axon) toward its tip (the synapse).
Here, the charge causes the neuron to release brain chemicals into the gap between neurons, known as the synaptic cleft. These molecules float over the space and bind to the receptors on neighboring cells. What happens next depends on the type of neurotransmitters released.
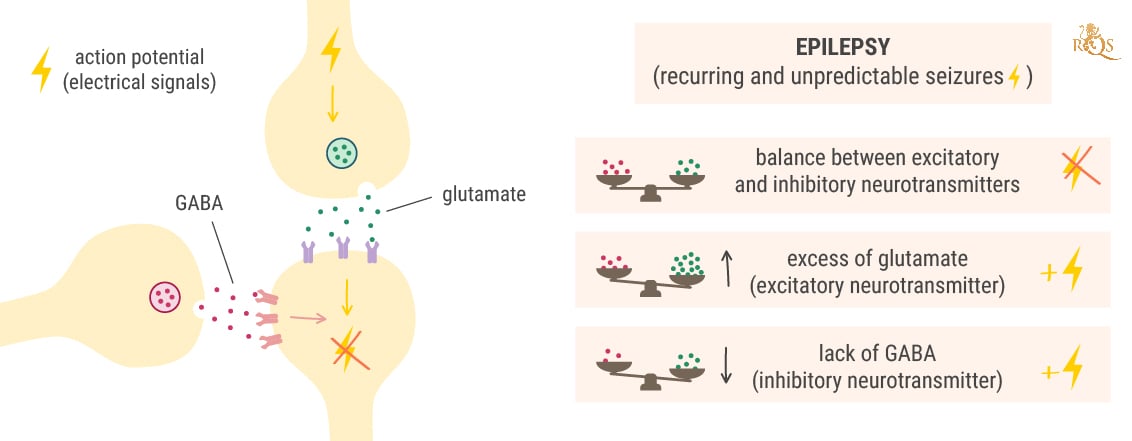
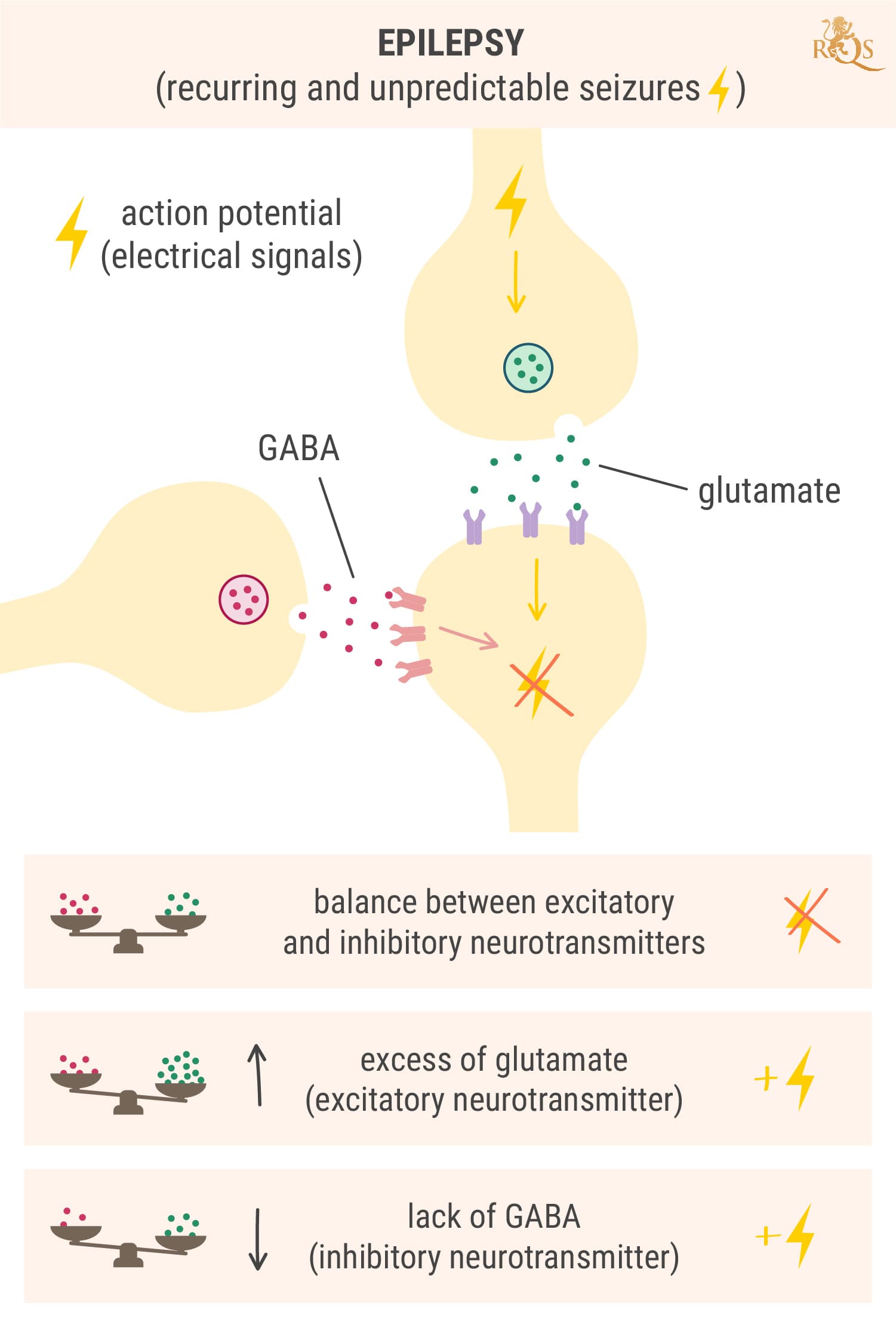
Glutamate (the brain chemical that excites cells) binds to the receptors on nearby neurons and forces their ion channels to open. This causes them to also become positively charged and carry the electrical message onward. In contrast, GABA (the brain chemical that dampens activity) slams the brakes on this process. It instructs nearby neurons to close their ion channels and shut down the electrical signal.
Seizures occur when neurotransmitter levels become awry. During a seizure, groups of neurons in certain regions of the brain become “hypersynchronous” and excitable, and start sending out electrical discharges over and over again.[5] This occurs because of either too much excitation (glutamate release) or too little dampening (reduced GABA release).
Genetic factors that cause long-lasting glutamate receptor activation or give rise to dysfunctional GABA receptors underpin epilepsy. A surge in neuronal excitability manifests as obvious seizure symptoms such as shaking and losing consciousness, as well as symptoms subjective to the patient, including irregular smells and sensations of fear.
How Epidiolex Combats Seizures
So, where does Epidiolex come into the picture? This cannabis-based medicine affects numerous molecular targets implicated in seizures. Researchers are still getting to grips with exactly how CBD works at a cellular level to quell excess excitability. Some of the proposed mechanisms include:
| TRPV1 | As a proposed cannabinoid receptor, CBD binds to TRPV1. This site works to modulate seizures, and ramps up glutamate release and increases in calcium. Although this mechanism drives seizures, the receptor enters a state of desensitisation after activation by CBD.[6] |
| T-type calcium channels | Calcium plays a major role in neurotransmitter release, and this receptor type causes an influx of calcium into the neuron when activated. CBD works to block these channels. |
| Serotonin receptors | The role of serotonin receptors remains unclear when it comes to epilepsy. However, CBD binds to some of these sites, and researchers believe this could underpin the molecule’s mechanism of action.[7] |
| Opioid receptors | Certain opioid receptors play a role in epilepsy, and CBD works to block them when present in high concentrations.[8] |
| GPR55 | Some researchers have named GPR55 the third cannabinoid receptor. This site works to modulate synaptic transmission, and CBD directly binds to it. |
| TRPV1 | As a proposed cannabinoid receptor, CBD binds to TRPV1. This site works to modulate seizures, and ramps up glutamate release and increases in calcium. Although this mechanism drives seizures, the receptor enters a state of desensitisation after activation by CBD.[6] |
| T-type calcium channels | Calcium plays a major role in neurotransmitter release, and this receptor type causes an influx of calcium into the neuron when activated. CBD works to block these channels. |
| Serotonin receptors | The role of serotonin receptors remains unclear when it comes to epilepsy. However, CBD binds to some of these sites, and researchers believe this could underpin the molecule’s mechanism of action.[7] |
| Opioid receptors | Certain opioid receptors play a role in epilepsy, and CBD works to block them when present in high concentrations.[8] |
| GPR55 | Some researchers have named GPR55 the third cannabinoid receptor. This site works to modulate synaptic transmission, and CBD directly binds to it. |
Epidiolex Side Effects
While ongoing research looks promising, some patients experience side effects when taking Epidiolex. These include:
| Drowsiness | Decreased appetite | Fatigue | Malaise |
| Rash | Insomnia | Infections | Drug interactions |
| Drowsiness | Decreased appetite |
| Fatigue | Malaise |
| Rash | Insomnia |
| Infections | Drug interactions |
What Is Epidiolex Used For?
Currently, the FDA has only approved the use of Epidiolex for seizures associated with two specific conditions. However, ongoing research continues to explore its efficacy in other maladies, including chronic pain and anxiety.
Epidiolex for Seizures
Epidiolex prescribing information published by the FDA strictly indicates its use in patients with two forms of epilepsy:
- Lennox–Gastaut syndrome: A severe form of epilepsy that manifests in early childhood and often leads to cognitive dysfunction.
- Dravet syndrome: A rare, drug-resistant form of epilepsy that shows symptoms in the first year of life.
The administration based the approval of Epidiolex on data collected from four key clinical trials consisting of a total of 550 participants with either Lennox–Gastuat or Dravet syndrome.[9] One of these studies, published in the journal Neurology, looked at the long-term safety and efficacy of Epidiolex as an add-on treatment for patients with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. Despite 11% of the participants leaving the trial due to side effects, 88% reported an improvement in their condition and a reduction in seizure frequency.[10]
Another of the key studies, this time published in the journal Neuropediatrics, investigated the long-term safety and efficacy of Epidiolex in patients with Dravet syndrome. A total of 264 patients participated in the study, and the researchers noted a reduction in seizure frequency and improvements in patient condition over a period of 48 weeks.[11]

Epidiolex for Chronic Pain
Ongoing studies are exploring the role of Epidiolex in the management of chronic pain. The ability of CBD to bind to serotonin receptors as well as transient receptor potential cation channels (TRP) receptors enables the cannabinoid to act on pathways involved in pain signalling and the inflammatory process.[12] However, a series of high-quality clinical trials are needed before agencies will consider approving Epidiolex for this purpose.
Epidiolex for Anxiety
Scores of anecdotal accounts describe CBD’s potential to ease the mind and soothe the body. A handful of human trials have also explored CBD as a treatment option for anxiety. Imaging studies have investigated how the cannabinoid alters blood flow in key brain regions,[13] and trials even tested the molecule in a simulated public speaking event.[14] CBD shows potential in this area, but more trials are needed to push agencies such as the FDA to approve Epidiolex for this use.
Is Epidiolex the Same As CBD Oil?
Although they share the same key ingredient, Epidiolex and CBD oil are not the same. For starters, each 100ml bottle of Epidiolex contains a highly standardised formula consisting of 10,000mg of CBD and inactive ingredients including dehydrated alcohol, sesame seed oil, strawberry flavoring, and sucralose—this never changes.
In contrast, CBD oils are available in a massive range of formulas. You’ll find different ingredients, flavors, and concentrations. CBD oils also contain more cannabis phytochemicals than Epidiolex, such as aromatic terpenes and additional non-psychotropic cannabinoids, like CBG and CBN, that work in synergy to create an entourage effect.[15]
Despite its lack of phytochemical diversity, the strict pharmaceutical manufacturing process used to create Epidiolex means patients receive exactly what they’re expecting every time. This standardisation leads to the accurate dosing and strict quality control required of products to earn FDA approval. For now, the FDA has limited Epidiolex for a short list of conditions. However, as research continues, it seems likely that this cannabis-based medicine will help to tame the symptoms of more conditions in the future.
- EPIDIOLEX® (cannabidiol) oral solution https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
- FDA Approved Drug | EPIDIOLEX® (cannabidiol) https://www.epidiolex.com
- FDA Approves First Drug Comprised of an Active Ingredient Derived from Marijuana to Treat Rare, Severe Forms of Epilepsy | FDA https://www.fda.gov
- The action potential in mammalian central neurons | Nature Reviews Neuroscience https://www.nature.com
- Synchronization and desynchronization in epilepsy: controversies and hypotheses - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- TRPV1 Channel: A Potential Drug Target for Treating Epilepsy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Use of Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Epilepsy: Efficacy and Security in Clinical Trials https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Delta opioid receptors in brain function and diseases https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Drug Trials Snapshots: Epidiolex | FDA https://www.fda.gov
- Long-term Safety and Efficacy of Add-on Cannabidiol (CBD) Treatment in Patients with Lennox Gastaut Syndrome in an Open-label Extension Trial (GWPCARE5) (P5.5-001) | Neurology https://n.neurology.org
- Long-term cannabidiol treatment in patients with Dravet syndrome: An open-label extension trial - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- An Update of Current Cannabis-Based Pharmaceuticals in Pain Medicine - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- P.3.006 Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on regional cerebral blood flow | Request PDF https://www.researchgate.net
- Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov