.

A Guide To International Cannabis Driving Laws
Cannabis driving laws vary widely depending on where you are. The safest option? Don't smoke and drive. However, if stopped, it is very important to know your rights. This is especially critical if you are a medical cannabis patient.
Cannabis and driving is still a loaded topic pretty much everywhere. What’s worse is that most countries do not have evidence-based THC limits established for drivers. As a result, the amount of THC in your system that qualifies as “drugged driving” varies depending on where you are.
While this list is by no means definitive, below is a short overview of how cannabis driving laws vary from country to country. By all means, check with an attorney if unsure. In general, it is better to be safe. That means, especially if you are a foreigner, don’t consume cannabis and drive. If caught and tested, you might be in for a ride you wish you skipped altogether.
WHY ARE TESTS USED?
There is considerable evidence that the consumption of cannabis affects motor and cognitive response in many people. At what level and how long after consumption, however, is the pressing question.
For this reason, the issue of testing for impairment from cannabis has long been controversial. Different bodily fluids can also produce different results. Further, all tests do not actually test for THC, but rather a metabolised form of the drug. This means that the psychoactive impact of THC may well have worn off.
Medical cannabis patients are the most vulnerable to such tests, both in employment and driving situations.

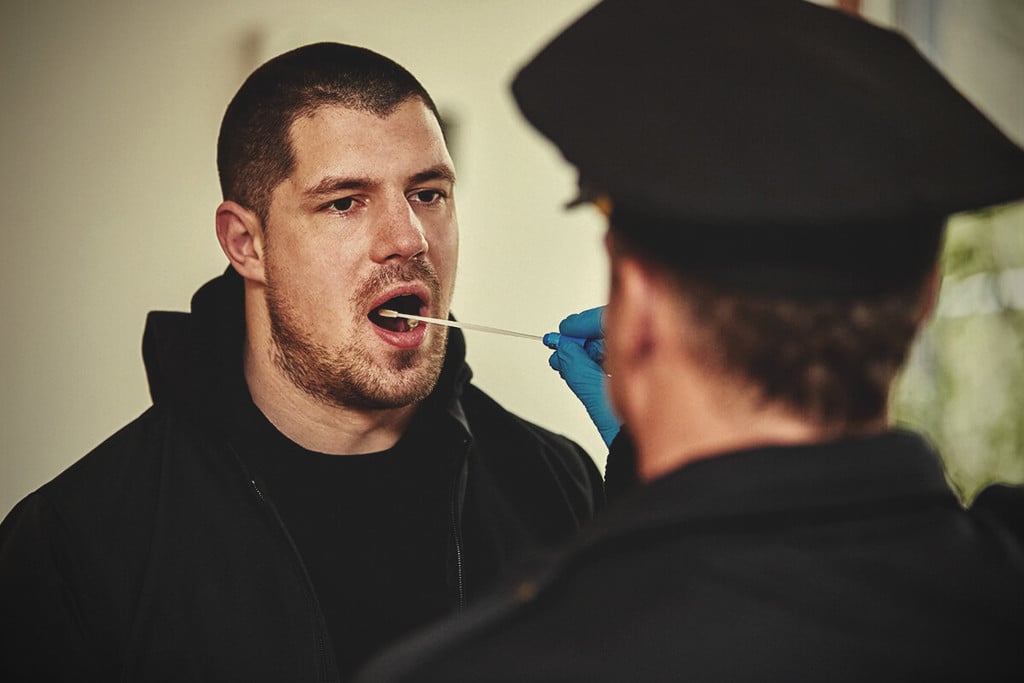
WHAT DO THE POLICE TEST FOR?
What gets tested also depends on where you are. Breathalyzers are beginning to be used by the police in the United States. Urine tests are also more common because of their widespread use in the employment sector. In other jurisdictions, blood tests are the only evidence that is court admissible.
However, even here, there is a great deal of controversy. Pot tests do not test for the presence of THC. Instead, they measure the level of THC-COOH. This is a metabolite of THC that is produced after the liver breaks down THC.
As with many drug tests, this means that you could fail, even if you haven’t smoked for days, or even weeks. It does not necessarily mean you are currently “high”. For these reasons, such tests are highly unreliable when used to determine current sobriety.
Daily users and patients are therefore at a huge risk of failing any sort of test that measures metabolites.
THE UNITED STATES
There is no federal mandate for THC and driving. Why? Cannabis is still not legal on a federal level. That said, legalizing states are trying to define their own laws. Bottom line? Check each state’s rules. Seven states now enforce legal marijuana metabolite limits for drivers. These include Colorado, Iowa, Montana, Nevada, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Washington state.
All these states, with the exception of Iowa, list legal THC thresholds for blood in existing drugged driving laws. Iowa, Nevada, Ohio, and Pennsylvania have also set legal THC and THC-COOH limits in urine.
Beware and be careful.
Drugged driving and alcohol-related driving are major crimes in the United States. If an accident involves property damage or injury to others, the penalties can include jail time. Refusing to take a test of any kind (blood or urine) is considered a positive response.
Finally, it is also likely that California’s recreational market (and cannabis driving laws) will have a huge impact nationally. The state has just outlawed the consumption of cannabis in a moving vehicle. For both drivers and passengers. It is already illegal to have an open bag of cannabis in the car.
Other states are very likely to follow California’s lead.
CANADA
There are no national standards set yet. However, it is very likely that a precise limit will be introduced by next July at the outset of the recreational market.
EUROPE
In Europe, there are so many discrepancies that there is no “norm”. Most EU states only test for active THC in the blood if stopped. However, some EU countries also measure THC-COOH. That is a non-psychoactive metabolite. Sixteen countries in Europe have set non-zero THC concentrations above which drivers can be prosecuted for driving under the influence. Of these countries, eleven enforce whole blood testing. This is the case across the Nordic states, Greece, Ireland, Eastern European countries, and the UK. Belgium, Germany, Luxembourg, and Slovenia all require blood serum tests.
The Netherlands has established limits on both THC in blood and blood serum.
However, no European countries have set THC limits for urine.
Some countries also require different tests, such as saliva. Others require urine. In some EU countries, tests are mandatory. In others, they are voluntary.
Finally, some countries skip tests altogether and rely on the officer’s visual interpretation of the scene. If he or she determines a test is required, drivers are then expected to submit to the same.
Across Europe, only blood tests can be used in court.
Penalties also vary across EU countries. They can range from fines to driving bans, which in some cases, can last for life.
EUROPEAN DRUGGED DRIVING PENALTIES BY COUNTRY
The right to drive in Europe is regulated not only by country, but by the EU itself. Member states issue driving licenses according to the Third Driving License Directive issued in 2006. This states that “driving licenses shall not be issued or renewed for applicants or drivers who are dependent on psychotropic substances”.
What does this mean on a country-by-country basis? Here is a sampling of legislation across Europe.
Austria
Anyone can be stopped on suspicion. A blood test must be taken at the hospital. There are no limits that qualify as “impaired”. Licenses can be suspended for at least four weeks. Fines range from €800-3,700.
Belgium
Oral fluid testing can be conducted at the stop. However, evidence must come from a hospital drug test. Levels are set not only for cannabis, but other drugs. Licenses can be suspended between one month to five years. Fines can range from €1,000-10,000.
Croatia
Police can test saliva or urine at the stop, however, evidentiary blood tests must be taken at a hospital. Cannabis is treated like other illegal drugs. There are no limits or guidelines in national driving legislation. Penalties include fines, license suspension, and even prison.
Czech Republic
Oral roadside testing can occur at the stop. However, blood must be taken at a hospital to prove “impairment”. Specific levels are also set. License suspension can occur from six months to a year for first time or minor violations. They can also be taken for up to ten years for more serious offenses. Prison is also a possibility if there has been a serious accident.
Denmark
Roadside testing is allowed, but again, drivers must take a blood test at the hospital if the conviction is to stand up in court. Unlike many other countries, those who have a medical prescription have a special dispensation. That said, impaired driving is impaired driving. If there is an accident, expect sanctions. These can range from license suspension, fines, and light prison terms of no more than 1.5 years.
Germany
The police’s right to stop and test depends on what state you are in. However, evidentiary tests are taken at the hospital. Worse, there are no limits specifying “impairment”. That said, there are basic guidelines which apply to cannabis, as well as other illicit drugs. License suspension can range from 1-3 months to permanent withdrawal. Prison, unless there is a serious accident, is not a regular punishment.
France
Roadside fluid testing is being introduced across the country. However, blood, saliva, and urine tests at hospitals are the only evidence admissible in court. There are no specific limits. Penalties include license suspension for up to three years, fines, and prison time. The latter is especially true if the driver is also drunk.
Italy
Blood tests are required, but roadside tests are allowed. There are no limits specified in Italian driving legislation. License suspension periods range from fifteen days to four years. Fines range from €1,500-6,000. Prison terms can also be imposed from six months to two years.

Luxembourg
Police can test at the roadside stop, but a blood test is required at a hospital for a conviction. There are limits for all illicit substances written into the law. License suspensions range from one month to life. Fines can range from €250-5,000. Prison terms range from eight days to three years.
Netherlands
Police are not allowed to ask for a roadside test. You have to take a blood test at a hospital. The test, however, is for “impairment” rather than to measure a specific level of metabolites in the blood. License suspensions can last for up to five years. Fines start at €6,000 and rapidly increase from here, especially if there has been bodily harm. Prison terms are also a possibility, particularly if the driver is reckless or if there is a fatality or injury.
Norway
Blood tests at the hospital are required, and the metabolite levels are set. Roadside tests are also allowed. License suspensions start at one year. Fines can be imposed and prison time can also last up to one year.
Poland
Police can test at the roadside, but the evidentiary test must be taken at a hospital or police station. There are no limits specified. Licenses can be suspended from 1-10 years. There are a wide variety of fines. Prison terms can last up to two years.
Portugal
Police may ask you to take a roadside test, but a hospital blood test is required for evidence that can be used in court. There are no limits specified. Upon conviction, licenses can be suspended from two months to two years. Fines depends on the severity of the offense. Prison terms are also possible, again, depending on severity. If there has been an accident due to negligence, this can be as long as three years.
Sweden
An evidentiary test is required. However, there is no liability if the drug is being taken with medical supervision. There are no limits specified. License suspension periods range from one month to three years. Forfeiture of the vehicle is also possible. Prison sentences are for a maximum of two years.
UK
Police can stop based on suspicion and administer an oral test. Evidentiary blood tests must be done at a police station. There are drug test limits that are predetermined by law. Penalties include a minimum one year prison sentence. Fines are unlimited. Prison terms can range up to fourteen years if there is a fatality.

HOW TO AVOID GETTING BUSTED
Obviously, preventive measures are better than actually having to prove your innocence. Here are a few tips to avoid such unpleasant encounters before they occur.
- Don’t drive while high.
- Do not smoke in the car.
- Do not have any open cannabis containers in the car with you.
- Don’t drive for at least four hours after ingesting cannabis with THC.
- Avoid driving on weekend nights, when more impaired people are on the road.
- Drive a few miles under the speed limit and keep your speed consistent.
- Clean your car on a regular basis; the smell of cannabis gives police the right to suspect you.
- If police ask you to admit to smoking cannabis, never answer - ever.
- If asked to take a voluntary test, refuse politely. In some European countries, this is a possible option. You can request to take a blood test if you are required to be tested.