.
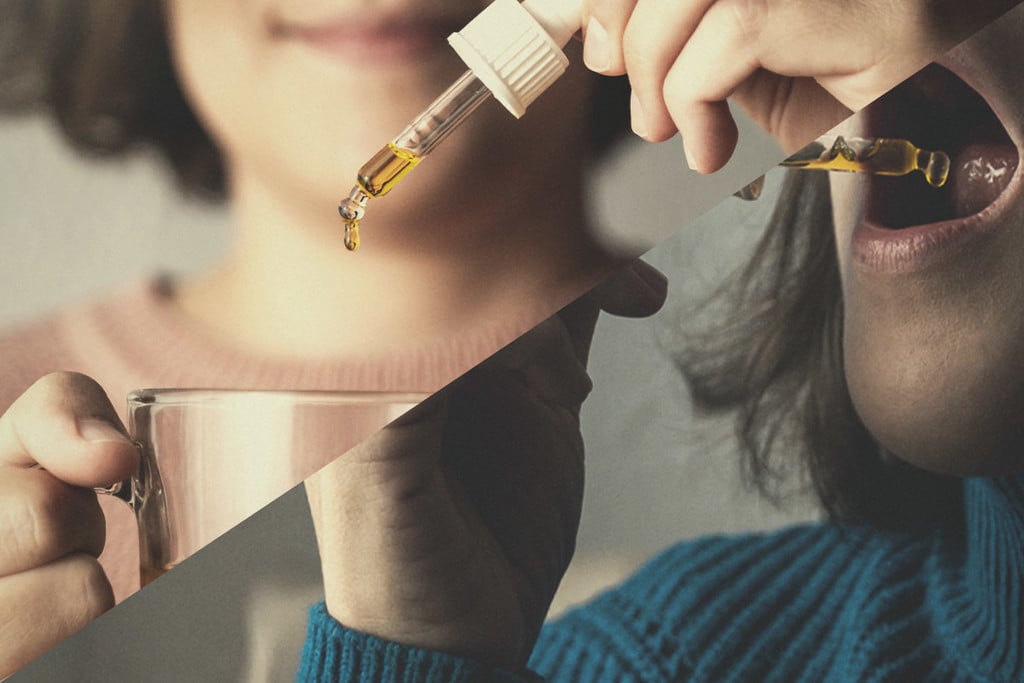

Oral vs Sublingual Cannabis: Which Intake Method Is Better?
Why does placing THC oil under the tongue feel different than eating a weed brownie? The answer lies in the route of administration. The sublingual route delivers THC straight into the bloodstream and lasts about as long as smoking, whereas the oral route has a longer onset and duration, and offers a more potent high. Which method is superior?
Contents:
There are myriad ways to consume cannabis, from smoking joints and hitting bongs to baking cakes in the kitchen. Each method offers unique advantages, and unique effects to boot.
Oral and sublingual administration both deliver cannabis via the mouth, but despite a similar means of access, these routes result in a dramatically different onset, duration, and intensity of effects.
Discover the key differences between oral and sublingual cannabis below, and how to harness these routes of administration to your benefit.
What Are the Alternatives to Smoking Cannabis?
Many cannabis users love smoking joints. The visceral sensation of harsh smoke in the lungs adds something to the experience. Plus, grinding, rolling, and lighting a joint are social rituals in their own right. There’s simply something meditative and familiar about the practice.
But some cannabis users have an aversion to smoking. Luckily for them, they can choose from a whole bunch of different ways to use the herb. Some of the best alternatives to smoking include:
- Vaping: Vaporising utilises lower temperatures than smoking. The lack of combustion results in fewer carcinogens and more of a herbal flavour.
- Edibles (oral): There are plenty of edibles to choose from, including cakes, gummies, capsules, tablets, and much more. This route of administration takes a while to set in, but the experience lasts much longer.
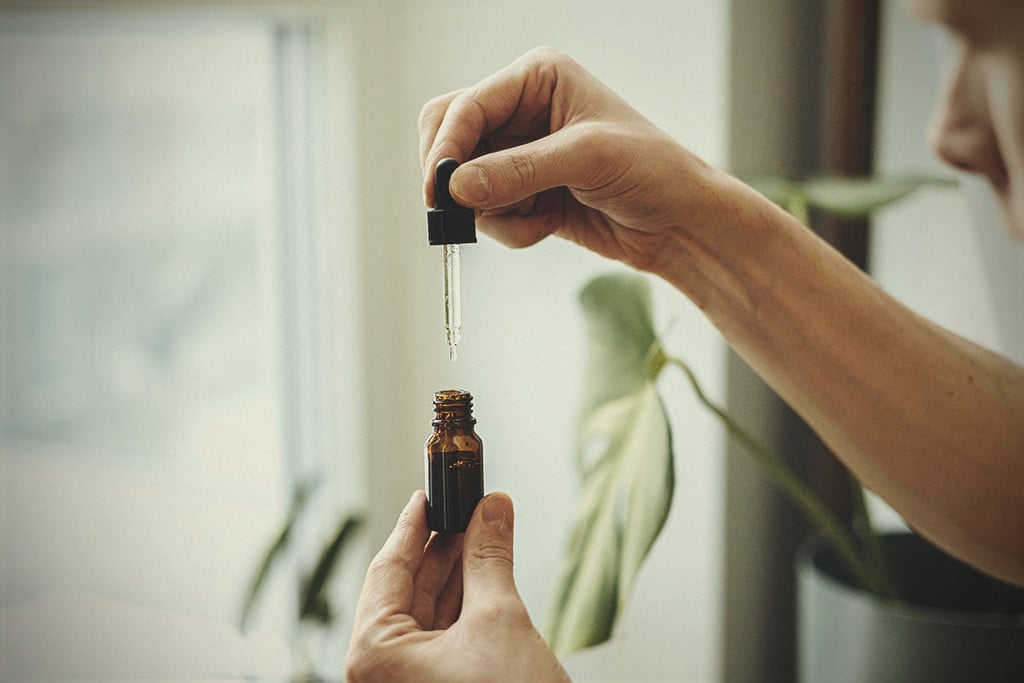
- Sublingual: This simply refers to placing tinctures, oils, extracts, or strips under the tongue, where they diffuse directly into the bloodstream.
What Is Oral Ingestion of Cannabis?
Never heard of oral ingestion? Think edibles. This route of administration simply refers to eating, drinking, or otherwise swallowing cannabinoids. Some users prefer to cook cannabis-infused brownies, whereas others value the simplicity of popping a couple of capsules.
Regardless of the vessel, orally consumed cannabinoids all end up in the same place: the stomach. This longer route sets edibles apart from other ways of consuming cannabis. Instead of directly entering systemic circulation, oral cannabinoids are subject to first-pass metabolism. This pathway involves processing in the liver, where our detoxifying organ converts THC into the potent 11-hydroxy-THC, alongside some other, inactive metabolites.
First-pass metabolism creates somewhat of a paradoxical situation. Oral administration only leads to the absorption of up to 20% of THC[1] consumed, but edibles result in a much more powerful effect. Why? Because 11-hydroxy-THC has much greater psychotropic potential. Not only does it make up for the THC lost in the gut and liver, but it exceeds the mind-altering wallop of smoked cannabis.


Benefits of Oral Ingestion
So, why do some cannabis users opt for brownies over bongs? The main benefits of oral marijuana intake include:
- Increased potency: People are drawn to edibles for their hard-hitting effects. Recreational users enjoy the psychedelic-like properties of 11-hydroxy-THC and find the metabolite takes them to places that regular THC cannot. Edibles also play an important role in a medicinal context, and help some medical marijuana users find more relief than with inhaled cannabis.
- Longer onset: Edibles take a while to kick in. The cannabinoids have to travel through the gut and liver, after all. While some people avoid edibles for this reason, others value this trait. You can pop in a capsule or gummy on the train ride home and be soaring once you enter your home. The build-up can add suspense to the experience and proves no big deal to those who have freed up their schedule.
- Longer duration: Edibles take longer to set in, but they also provide a longer-lasting psychotropic effect. Overall, the experience tends to last between 6–8 hours. Peak blood concentrations of 11-hydroxy-THC occur at around three hours, after which users experience a pleasant afterglow.
What Is Sublingual Cannabis Intake?
Ever see people take CBD oil under the tongue? That same principle applies to THC oil and tinctures too—only, unlike CBD, these products will get you sufficiently stoned.
Sublingual intake simply refers to placing a substance under the tongue. This might sound strange—why not just swallow it? Well, the tissue under the tongue serves as a semi-permeable barrier. Lipophilic molecules such as THC readily diffuse through this layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue into the capillaries below.
This route grants cannabinoids immediate access to the bloodstream. These capillaries belong to the systemic venous system. This means sublingually applied molecules sidestep first-pass metabolism. THC passes through the blood–brain barrier without encountering enzymes in the liver that would otherwise catabolise it into 11-hydroxy-THC. Plus, much more THC reaches systemic circulation. Sublingual cannabis administration vastly increases the bioavailability[2] of cannabinoids.

Benefits of Sublingual Cannabis Intake
Sublingual intake has soared in popularity in the cannabis space. The main benefits of sublingual cannabis intake include:
- Rapid onset: Sublingual THC takes effect within a matter of minutes. It shares a similar onset to smoking and vaping, but with no inhalation involved.
- Easy to judge: Various factors can impact the bioavailability of oral cannabis, making it unpredictable. Sublingual products offer more accuracy and fewer fluctuations. If you take a 10mg THC sublingual strip, you’ll have a good idea of what will make it into your bloodstream.
- You get what you’re given: You took THC, and the sublingual method respects that choice. Instead of getting the liver involved and dosing you with a much more powerful drug, sublingual marijuana administration keeps THC intact and familiar.
- Fast duration: Sometimes, you just want to get high without sacrificing the rest of your day. Sublingual cannabis offers a swift psychotropic experience. You can sit back and enjoy it for an hour or two, after which you can get cracking on with whatever you have planned for the rest of the day.
Oral vs Sublingual Cannabis: Key Distinctions
Oral and sublingual administration offer two completely different ways to experience cannabis. Sure, they both involve inserting cannabis products into the mouth, but the similarities end there. Check out the key differences between both methods below for a quick summary of their effects.
| Onset | How long does it take for THC oil to work orally? What about brownies? Or capsules? When it comes to oral intake, expect to wait between 30–60 minutes, at least. If you’ve just dosed sublingually, expect to feel the effects almost right away (within a few minutes). |
| Bioavailability | Bioavailability refers to the amount of a substance that makes it to systemic circulation. Oral cannabis offers poor bioavailability—only around 20% of cannabinoids make it into the bloodstream. Sublingual administration, on the other hand, offers at least three times the absorption rate[3]. |
| Duration |
Duration refers to how long the high lasts. An oral cannabis high can last up to 8 hours, so you better buckle up and get ready to enjoy the ride after you eat an edible. In contrast, the sublingual marijuana experience ends much sooner. Expect to stay baked for an hour or so before touching back down to Earth. |
| Effects |
Edible cannabis offers an intense and unique experience. Don’t expect a similar ride to smoking a joint. It’s an introspective and powerful experience not always suited to parties or social gatherings. Sublingual products offer a much different effect comparable to smoking or vaping weed. |
| Onset |
|
How long does it take for THC oil to work orally? What about brownies? Or capsules? When it comes to oral intake, expect to wait between 30–60 minutes, at least. If you’ve just dosed sublingually, expect to feel the effects almost right away (within a few minutes). |
| Bioavailability |
|
Bioavailability refers to the amount of a substance that makes it to systemic circulation. Oral cannabis offers poor bioavailability—only around 20% of cannabinoids make it into the bloodstream. Sublingual administration, on the other hand, offers at least three times the absorption rate[3]. |
| Duration |
|
Duration refers to how long the high lasts. An oral cannabis high can last up to 8 hours, so you better buckle up and get ready to enjoy the ride after you eat an edible. In contrast, the sublingual marijuana experience ends much sooner. Expect to stay baked for an hour or so before touching back down to Earth. |
| Effects |
|
Edible cannabis offers an intense and unique experience. Don’t expect a similar ride to smoking a joint. It’s an introspective and powerful experience not always suited to parties or social gatherings. Sublingual products offer a much different effect comparable to smoking or vaping weed. |
Sublingual vs Oral Consumption: Which Method Is Best for THC and CBD?
Next time you’re deciding between sublingual tincture vs edibles, really think about what kind of experience you want to have. After all, neither of these methods is better or worse than the other—it just depends on your preference. If you’re looking for a light, quick, and efficient high, put some THC oil under your tongue. If you want to dive deep and spend the next few hours staring at the ceiling, cook up a batch of brownies and wait for them to kick in.
DisclaimerWhen consumed, THC metabolizes into 11-hydroxy-THC, which enters the body through the stomach and liver, resulting in a significantly stronger effect due to its increased affinity for CB1 receptors in the brain.
Ensure accurate portion control. Begin with small doses and gradually increase to develop tolerance.
Remember: Set and Setting will help you deal with various situations.
Stay Cultivated.
- Human Cannabinoid Pharmacokinetics https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Sublingual mucosa as a route for systemic drug delivery https://innovareacademics.in
- Sublingual mucosa as a route for systemic drug delivery https://innovareacademics.in