.
CBD, Serotonin, and Anxiety
As cannabis consumers, some of us have experienced certain improvements in our mood and degree of relaxation with specific cultivars. But nowadays, scientists are starting to explore several of the cannabis plant’s compounds for their effects on depression and anxiety—and it seems serotonin could play a major role
WHAT IS SEROTONIN?
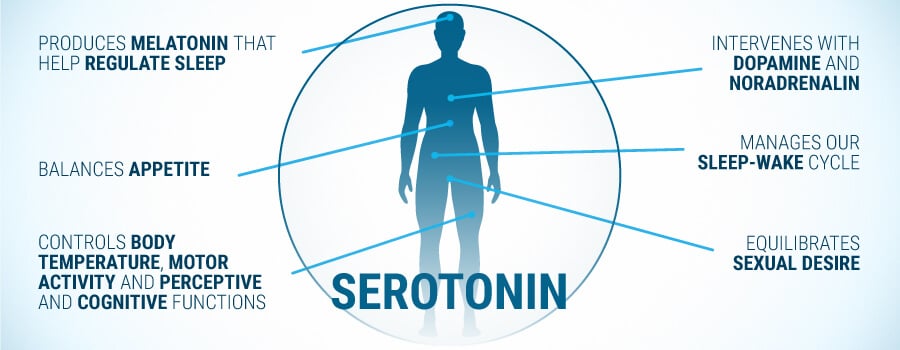
The human body uses neurotransmitters to perform various functions. These “chemical messengers” are the main tools in the central nervous system’s neuronal communication. Serotonin is one such neurotransmitter present in the brain, intestines, and bones. Among other functions, it works to regulate mood, nausea, appetite, bone health, sleep, emotions, and even sexual function. The vast majority of serotonin can be found in the gastrointestinal tract
Serotonin is produced through a two-step conversion process from the essential amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan can be found in common foodstuffs like cheese, red meat, and nuts. A lack of this amino acid in our diet may result in reduced serotonin levels. This, in turn, could be linked to anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. It's because of factors like this that our diet is so closely linked to our mood and emotions.
HOW DOES CANNABIS INTERACT WITH SEROTONIN?
The relationship between cannabis and serotonin is very interesting. Cannabinoids may stimulate certain serotonin receptors while potentially inhibiting others[1].
This leads to the conclusion that cannabinoids may increase serotonin—and other neurotransmitters—levels in certain conditions, and reduce them in others. A migraine, for example, is a condition that correlates with decreased serotonin levels in the brain[2]. In this situation, the activation of reuptake inhibitory receptors could be part of the solution. When one consumes THC, it activates serotonin receptors while inhibiting its reuptake[3]. Studies have even observed that certain cannabis strains could potentially have an impact on migraine [4].
Once one recognises the importance of serotonin in mood and various disorders, and the impact of cannabis on serotonin levels, it’s easy to see why cannabis-derived molecules are being studied in regard to certain mental and neurological illnesses.
HOW CANNABIS INTERACTS
In 2016, a study[5] was performed where mice were administered several chemicals that mimic the endocannabinoid anandamide. The interesting part was that when the researchers artificially blocked the serotonin receptors, the potential antidepressive effects of these substances were no longer noticeable. This further suggests that cannabinoids and the serotonergic system are in fact linked".
The same study [6] also showed how increasing endocannabinoid levels in the body made antidepressants more effective. The study also found that blocking CB1 receptors would completely stop the antidepressants from working.
This demonstrates how the endocannabinoid and the serotonergic systems work together in helping us achieve homeostasis. It also shows that if there is going to be a medicine developed, these two systems will have to be stimulated in a way that is balanced and supportive to the other. So is cannabis the future of antidepressants?
MARIJUANA AND ANXIETY
When comparing the anxiety levels of 50 individuals who smoked cannabis regularly with 50 who didn't smoke at all, a study[7] showed some interesting results. The patients who smoked marijuana experienced potentially lower levels of anxiety than those who didn't. A 2012 paper[8] assessed multiple studies that looked into CBD as an anti-anxiety medication. This research served as a pioneering step in the field of CBD science, however, more studies are needed to determine how CBD impacts our psychological and physical state
Before you embark on using cannabis for holistic purposes, it's important to know what you're doing. You should always consult your physician before using any substance for a potentially therapeutic purpose. Despite cannabis being prescribed as a treatment for depression/anxiety in some regions, this plant–disease relationship is actually under current study, requiring much more research.

If you decide to consume cannabis under an anxiety-related scenario, it's essential to pay attention to the THC and CBD levels of each strain. You should note that every strain will have a different effect on different people. Given the non-intoxicating profile of CBD, pure CBD strains (without THC), CBD-dominant, or balanced THC:CBD strains could theoretically be more adequate to return a homeostatic effect.
For example, Euphoria, Painkiller XL, and Stress Killer are three CBD-rich strains with mild THC levels to boot. The first two mentioned have 9% THC, and Stress Killer has a content of 11%.
Like many other scientific queries related to cannabis, so much more research is needed to confidently provide advice on the exact way to use cannabis as a treatment for various psychological disorders. What is encouraging, however, is that cannabis is composed of numerous chemicals, some of which also seem to interact with serotonin. In the future, we’re bound to see this relationship fleshed out further.
- Descending serotonergic and noradrenergic systems do not regulate the antipruritic effects of cannabinoids https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Serotonin Syndrome versus Cannabis Toxicity in the Emergency Department https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Patterns of medicinal cannabis use, strain analysis, and substitution effect among patients with migraine https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 modulates serotonin-dependent emotional behaviour http://www.europeanneuropsychopharmacology.com
- Involvement of endocannabinoids in antidepressant and anti-compulsive effect of fluoxetine in mice http://www.sciencedirect.com
- Antianxiety effect of cannabis: involvement of central benzodiazepine receptors https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent, as an anxiolytic drug https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov